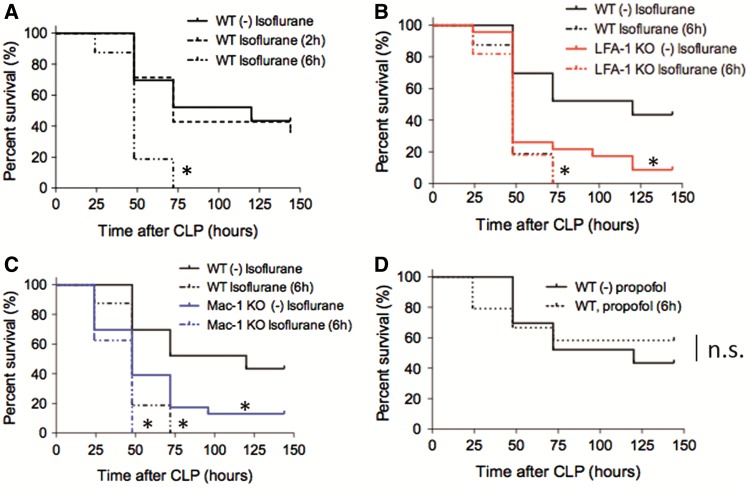
FIG. 1.
The impact of isoflurane exposure on mortality in experimental polymicrobial abdominal sepsis. A–C, The outcomes of polymicrobial abdominal sepsis induced by CLP in WT mice without isoflurane exposure (n = 25), with isoflurane exposure for 2 h (short exposure, n = 14) and 6 h (long exposure, n = 20), LFA-1 KO mice without isoflurane exposure (n = 24), LFA-1 KO mice with isoflurane exposure for 6 h (n = 16), Mac-1 KO mice without isoflurane exposure (n = 24) and Mac-1 KO mice with isoflurane exposure for 6 h (n = 15) are shown. D, The outcomes of mice after CLP in WT mice with propofol exposure (n = 20) or without propofol exposure (n = 20) for 6 h. Statistical significance was evaluated using Log-rank test. * and ** represent P < .05 and .01, respectively versus WT without isoflurane (or propfol). CLP, cecal ligation and puncture.