Table 1.
Nanosized delivery systems for anti-inflammatory polyphenols.
| Bioactive Principle | Nanovector | Type of Delivery System | Experimental Model | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Quercetin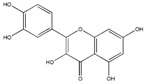
|
Nanoparticles | NP of soya lecithin, Tween-80 and PEG | In vivo (rats) | [76] |
| PLGA NP containing quercetin | In vitro | [78] | ||
| Eudragit-polyvinyl alcohol quercetin-loaded NP | In vitro | [79] | ||
| Quercetin-PLGA NP | In vivo (rats) | [80] | ||
| Nanocapsules | Lipid-coated NC | In vitro | [77,78] | |
| Quercetin-PLGA NC | ||||
Resveratrol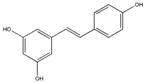
|
Nanoparticles | PLGA NP containing resveratrol | In vivo (Wistar male rats) | [82] |
| Eudragit RL 100 NP | In vitro/In vivo | [83] | ||
| Carboxymethyl chitosan NP | In vitro/In vivo (rats) | [84] | ||
| Solid lipid nanoparticles | SLN with a controlled release profile | In vitro | [85] | |
| Resveratrol loaded SLN | In vivo (Wistar male rats) | [86] | ||
| Cyclodextrins | CD-based nanosponges | In vitro | [87] | |
Ellagic acid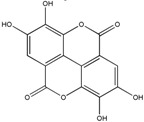
|
Nanoparticles | Ellagic acid-loaded PLGA NP | In vitro | [88] |
| PLGA-PCL ellagic acid NP | In vivo (rats with induced nephrotoxicity) | [89] | ||
Curcumin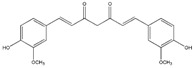
|
Nanoparticles | Hydrogel/glass | In vivo (rats with post-traumatic osteoarthritis) | [96] |
| Nanoemulsions | o/w nanoemulsion containing curcumin in the oil phase | In vitro | [98] | |
| Lipid nanoparticles | Lecithin liposomes | In vivo (rats) | [100] |
NP, nanoparticles; PEG, polyethylene glycol; PLGA, polylactic-co-glycolic acid; NC, nanocapsules; SLN, solid lipid nanoparticles; CD, cyclodextrins; PCL, polycaprolactone; o/w, oil in water.
