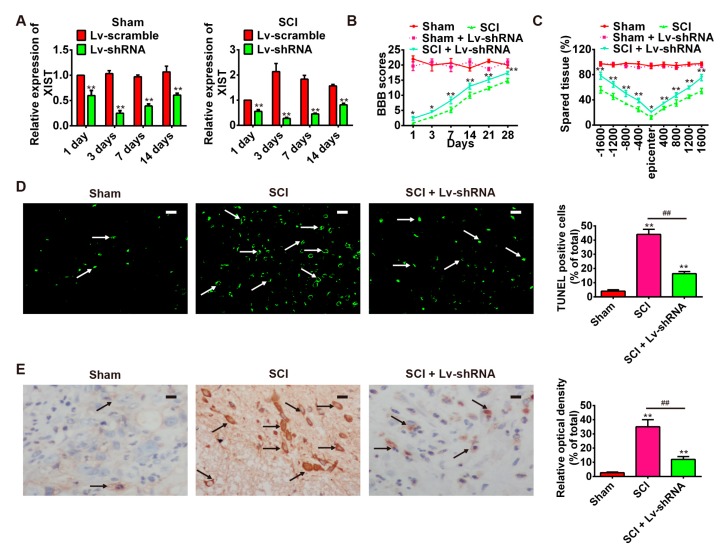
Figure 3.
Attenuation of SCI following knockdown of lncRNA-XIST. Rats were randomly divided into four groups: sham + Lv-shRNA; sham + Lv-Scramble; SCI + Lv-Scramble, and SCI + Lv-shRNA. (A) LncRNA-XIST expression at 1, 3, 7, and 14 days post-injury in spinal cord tissue of groups. n = 3/group/time point. (B) BBB scores of sham, sham + Lv-shRNA group, SCI group and SCI + Lv-shRNA group (n = 3/group/time point). (C) Quantification of lesion size within the injury site, and measurement of the distance between points 1600 μm rostral and caudal to the epicenter, seven days post-injury (n = 3/group/time point). (D) TUNEL staining of neuronal apoptosis in spared tissues of the SCI group and SCI + Lv-shRNA group (n = 4/group). The white arrows point out TUNEL-positive cells. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01 vs. the sham group, ## p < 0.01 vs. the SCI group. Data are means ± SEM. Lv-shRNA treatment significantly reduced neuronal apoptosis following SCI. (E) The expression of cleaved caspase-3 in SCI group and SCI + Lv-shRNA group was detected by immunohistochemistry staining (n = 4/group). The black arrows indicate cells stained positive with anti-cleaved caspase-3. Lv-shRNA treatment significantly reduced the expression of cleaved caspase-3 after SCI. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01 vs. the sham group, ## p < 0.01 vs. the SCI group. Image analysis was performed using Image-Pro Plus 4.5 software (Media Cybernetics, Silver Spring, MD, USA). Data are the mean values ± SEM. Scale bars in (D,E) 20 μm.