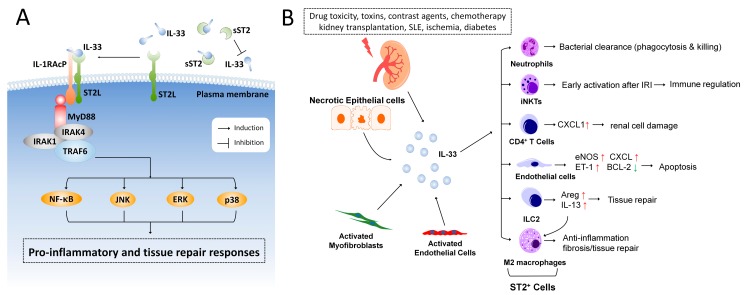
Figure 1.
IL-33/ST2 signaling in renal injury. (A) IL-33 binds to the receptor complex comprised of ST2L and IL-1RAcP on the cell membrane and induces recruitment of MyD88, IRAK1, IRAK4 and TRAF6, thereby activating the downstream NF-κB, JNK, p38, and ERK pathways. The extracellular soluble form of ST2 (sST2) binds IL-33 as a decoy receptor and has been postulated to be a biomarker in various inflammatory diseases; (B) Exogenous factors (such as drug toxicity, toxins, contrast agents, and chemotherapy), kidney transplantation, and diseases associated with nephropathies (SLE, renal ischemia, and diabetes) lead to upregulation of IL-33 in the renal tissues. Upon injury, necrotic epithelial cells, activated myofibroblasts, or endothelial cells release IL-33, triggering an inflammatory response and tissue repair processes by targeting the ST2-expressing cells.