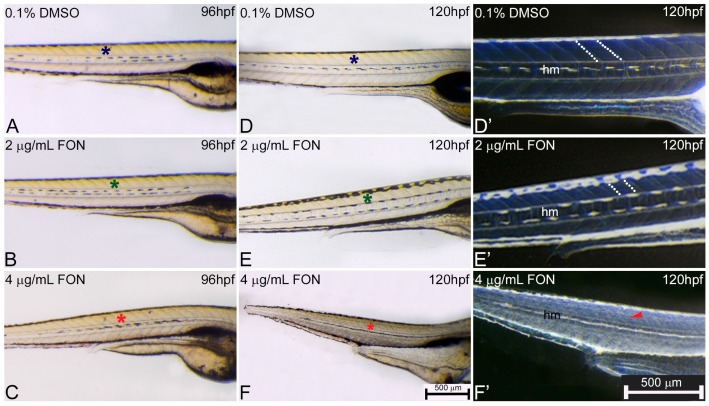
Figure 5.
Abnormal somitic, myotome and horizontal myoseptum phenotypes are described in triadimefon exposed zebrafish embryos. Representative morphological evaluation of zebrafish control (n = 92) and triadimefon treated embryos (80 and 89 embryos examined respectively) (A–C) at 96 hpf, and (D–F, D’–F’) from 96 to 120 hpf. At triadimefon concentrations of 2 and 4 μg/mL somitic and myotome development appear to be normal (left panel; green and red asterisks in B and C). One day later (middle panel), gross morphology evaluation shows no alterations of the myotome and somitic structures in 2 μg/mL triadimefon treated embryos (green asterisk in E). However, 4 μg/mL triadimefon embryos at 120 hpf present severe altered somitic structures with no clear boundaries (89/89) and disorganized muscle fibers (red asterisk in F) (85/89). Inversion of D–F embryo figures (left panel; D’–F’) reveals the absence of clear somitic boundaries (red arrowhead in F’) compared to 2 μg/mL triadimefon—treated and control embryos (white dotted region in E’). The horizontal myoseptum (hm) is normally developed in 0.1% DMSO control and 2 μg/mL triadimefon—treated embryos (D’,E’) but severely hypoplastic in embryos exposed to 4 μg/mL triadimefon (F’). FON, triadimefon. Embryos in A–F are shown to the same scale (bar = 500 µm in F) while embryos in D’–F’ are shown to the same scale (bar = 500 µm in F’).