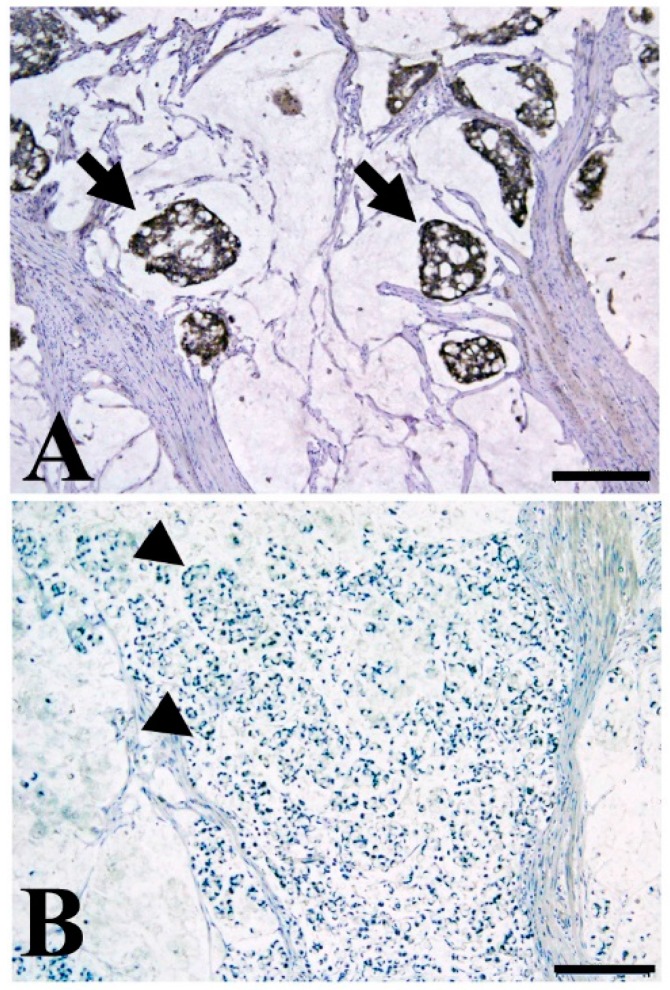
Figure 2.
Representative immunohistochemical staining of mucinous colon cancer with TMEM207 immunoreactivity (A) and without immunoreactivity (B); (A) Note the strong immunoreactivity to the specific antibody to TMEM207 in mucinous carcinoma with favorable prognosis (stage III, disease-free survival of over 60 months). Arrow indicate the TMEM207 immunoreactivity in mucinous carcinoma cells; (B) Little or no TMEM207 immunoreactivity was found in patients with poor prognosis. Arrow head indicate the negative TMEM207 staining. Archival pathological colorectal cancer tissues including mucinous carcinoma were immunostained with a conventional rabbit antibody to the synthetic peptide VNYNDQHPNGW (amino acid residues 40–50 of TMEM207). Details of the immunohistochemical staining procedure were described previously [77]. Briefly, antigen retrieval in deparaffinized tissue slices was performed with 0.25% trypsin for 5 min at 37 °C. After incubation for 30 min in 10% normal goat serum, the slides were incubated with various antibodies overnight at 4 °C. We used the ImmPRESS Polymerized Reporter Enzyme Staining System (Vector Laboratories Inc., Burlingame, CA, USA). The present study was conducted in accordance with the ethical standards of the Helsinki Declaration in 1975, after obtaining approval from the Institutional Review Board of the Gifu University Graduate School of Medicine (specific approval number 25-81). Immunoreactivity was based on examination of five high-power (×400) microscopic fields or the total tumor (when the tumor was smaller than five fields) for each case. Tumors showing strong immunoreactivity in >5% of cancer cells were considered positive. The scale bar represents 200 µm.