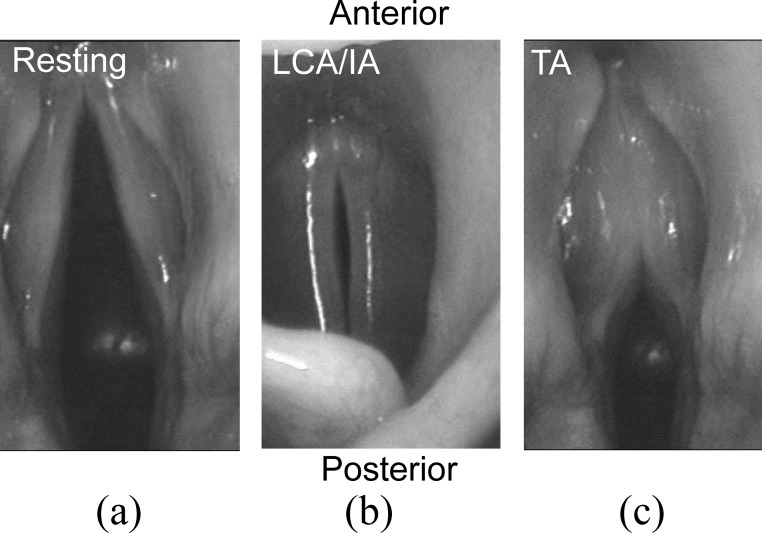
FIG. 3.
Activation of the LCA/IA muscles completely closes the posterior glottis but leaves a small gap in the membranous glottis, whereas TA activation completely closes the anterior glottis but leaves a gap at the posterior glottis. From unpublished stroboscopic recordings from the in vivo canine larynx experiments in Choi et al. (1993).