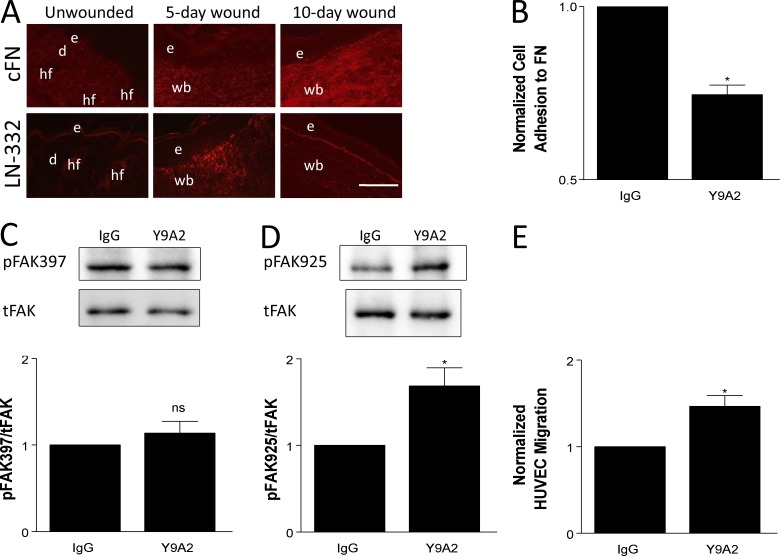
Figure 7.
Inhibiting the ligand-binding function of α9β1 abrogates cross-suppression of α3β1. (A) Immunostaining for cFN (top) or LN-332 (bottom) on cryosections from unwounded skin, 5-d wounds, and 10-d wounds of control mice. LN-332 is up-regulated by 5 d after wounding, whereas cFN is most abundant in 10-d wounds. n ≥ 4 mice per time point. Bar, 100 µm. d, dermis; e, epidermis; hf, hair follicle; wb, wound bed. (B–E) MK cells were treated with 10 µg/ml Y9A2 (α9β1 function-blocking antibody) or mouse IgG as control. (B) Treated MKα3−/α9+ cells were analyzed in adhesion assays to validate that Y9A2 reduced α9β1 binding to cFN. (C and D) Cell lysates from treated MKα3+/α9+ cells were assayed by immunoblot for FAK phosphorylation at tyrosine residues Y397 (C) and Y925 (D), as indicated. Graphs show quantitations from three independent experiments. tFAK, total FAK. (E) Transwell assays were performed as in Fig. 1 to compare the HUVEC migration response to conditioned media from treated MKα3+/α9+ cells. Data are normalized to the IgG control. Means ± SEM are shown. n ≥ 3 independent experiments. A Student’s t test was used. *, P < 0.05; ns, not significant.