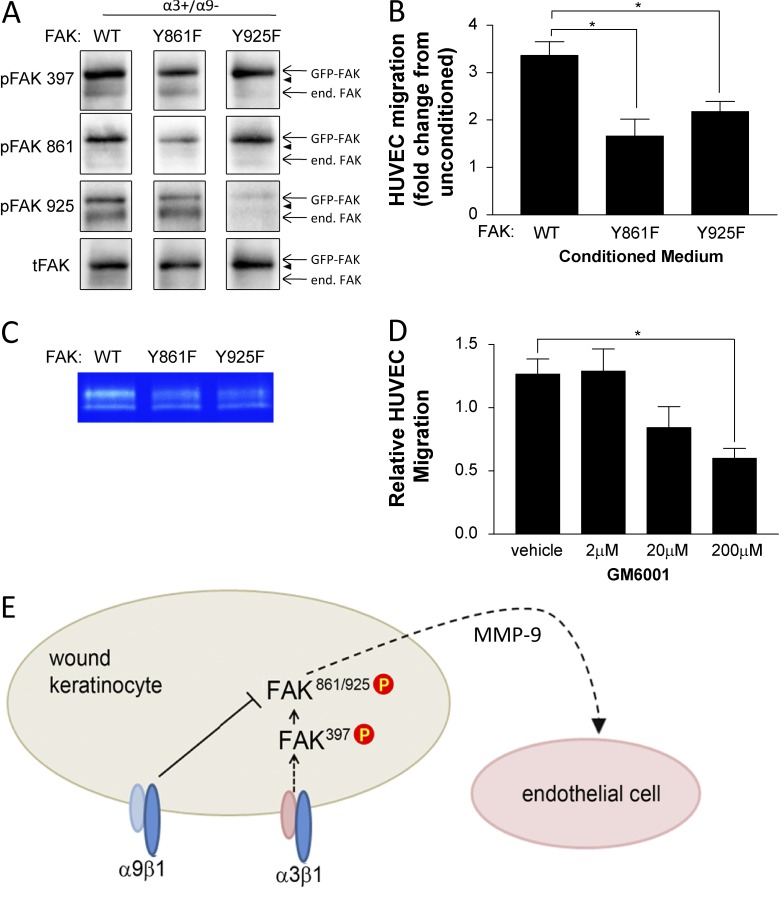
Figure 9.
Perturbation of FAK phosphorylation at Y861 or Y925 in α3β1-expressing keratinocytes reduces MMP-9 secretion and cross talk to endothelial cells. (A and B) MK α3+/α9− cells were infected for 24 h with adenovirus expressing GFP-tagged FAK:WT, FAK:Y861F, or FAK:Y925F and then grown to confluence on collagen. Cells were lysed to assess expression and phosphorylation of GFP-FAK fusion proteins (A), or conditioned medium was harvested and HUVEC migration response was assessed as in Fig. 1 (B). (A) Representative immunoblots confirm comparable expression of GFP-FAK variants and appropriately reduced phosphorylation of the mutated tyrosine. Arrowheads indicate positions of 130-kD markers. end. FAK, endogenous FAK; tFAK, total FAK. (B) Graph shows HUVEC migration in response to conditioned medium from GFP-FAK–infected MK cells relative to unconditioned media as a baseline (set to 1.0). (C) Secreted MMP-9 was assessed by gelatin zymography of MK-conditioned medium from α3+/α9− cells infected with wild type (WT) or mutant FAK adenoviruses. A representative zymograph from three independent experiments is shown. (D) Conditioned medium from MKα3+/α9− cells was treated with the MMP inhibitor GM6001, and the HUVEC migration response was assessed. Means ± SEM are shown. n = 3 independent experiments. One-way analyses of variance followed by Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test were used. *, P ≤ 0.05. (E) Model showing how α9β1 exerts its suppressive effect on α3β1 signaling downstream of FAK autoactivation at the point of Src-mediated phosphorylation of FAK Y861/Y925, leading to reduced cross talk to the endothelium partly through reduced secretion of MMP-9. P, phosphorylation.