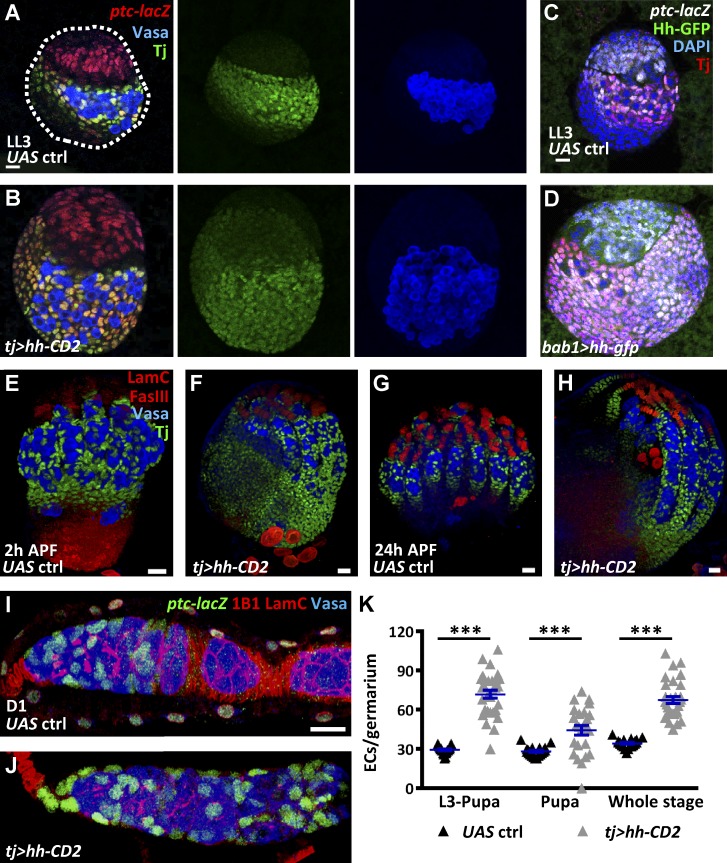
Figure 4.
Overexpression of Hh promotes IC formation leading to expansion of escort cells. (A and B) Late-L3 (LL3) control (ctrl; A) and tj>hh-CD2 gonads (B) with Vasa (blue, PGCs), ptc-lacZ (red, an Hh signaling reporter), and Tj (green, ICs). Dashed line in A outlines the gonad. (C and D) LL3 control (ctrl; C) and bab1>hh-gfp gonads (D) with GFP (green), ptc-lacZ (gray), Tj (red), and DAPI (blue, DNA). (E–H) Control (E and G) and tj>hh-CD2 pupal ovaries (F and H) with Vasa (blue), LamC (red, TF and cap cell nuclear envelopes), FasIII (red, stalk cell membranes), and Tj (green) at 2 (E and F) and 24 h (G and H) after puparium formation (APF). (I and J) 1-d-old (D1) control (I) and tj>hh-CD2 ovaries (J) with ptc-lacZ (green, escort cells), Vasa (blue, germ cells), 1B1 (red, fusomes and follicle cell membranes), and LamC (red). Bars, 10 µm. (K) Escort cell (EC) number per germarium of D1 control and flies with hh-CD2 overexpression driven by tj-GAL4 from L3 to pupal stages, during the pupal stage, or throughout development (whole stage). Statistical differences were analyzed by two-tailed t-test. Error bars represent SEM. ***, P < 0.001.