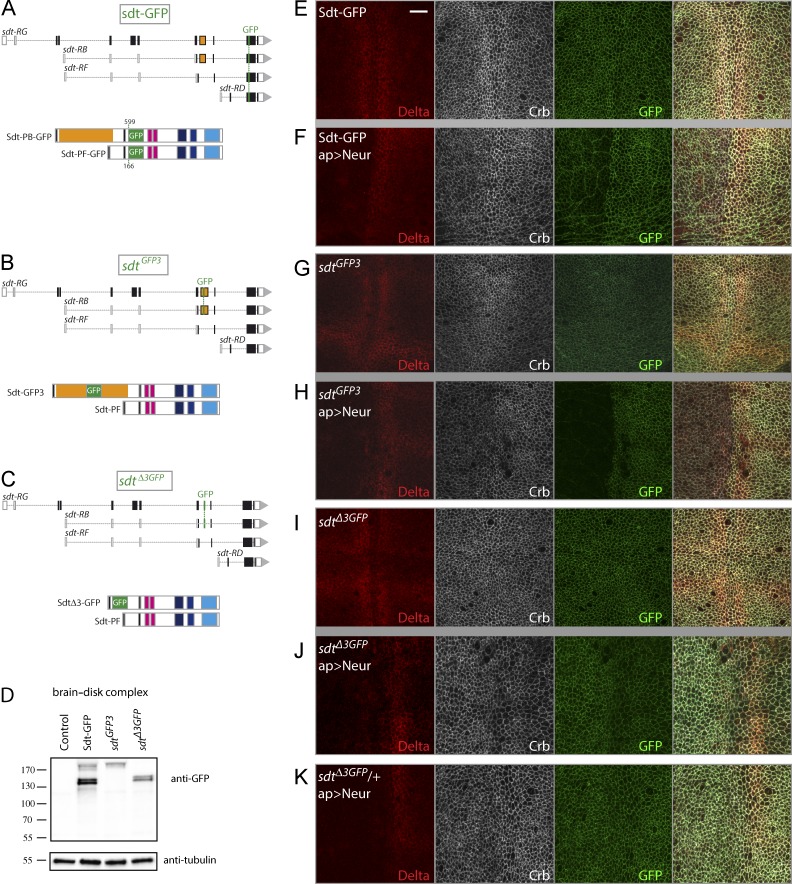
Figure 3.
Isoform-specific down-regulation of Sdt by Neur. (A) Structure of Sdt-GFP isoforms. GFP was inserted into a common exon (top) at amino acid position 599 in Sdt-PB and 166 in Sdt-PF (bottom). (B and C) Structure of the sdt alleles produced by CRIPSR-mediated HR. In sdtGFP3, GFP was inserted at amino acid 188 of Sdt-PB within Exon3 to produce Sdt-GFP3 (B). In sdtΔ3GFP, GFP replaced the sequence of exon 3, leading to the synthesis of SdtΔ3-GFP (C). These two alleles should not modify the synthesis of Sdt-PF. (D) Western blot analysis of brain–disk complexes from Sdt-GFP, Sdt-GFP3, and SdtΔ3-GFP larvae (control: wild-type larvae). As expected, Sdt-GFP3 and SdtΔ3-GFP comprise a subset of the Sdt-GFP isoforms. Molecular mass (kD) markers are shown on the left. (E–K) Neur induced the down-regulation of Sdt-GFP (GFP, green; E and F) and Sdt-GFP3 (G and H) but not SdtΔ3-GFP (I and J). Although Neur targeted Dl (red) for degradation independently of the Sdt isoforms, low Crb levels were detected in sdt-GFP and sdtGFP3 larvae but not in sdtΔ3GFP larvae. Thus, Neur regulates Crb indirectly via Sdt. Ectopic Neur down-regulated Dl, whereas Crb levels remained unchanged in heterozygous sdtΔ3GFP/+ larvae (K) as in sdtΔ3GFP larvae (J), despite the presence of endogenous Neur-sensitive Sdt from the wild-type locus. Thus, Neur-resistant SdtΔ3-GFP appeared to be sufficient to stabilize Crb. Bar, 10 µm. ap, apterous.