Figure 2. Photodynamic diagnosis of orthotopic mouse bladder cancer in vivo.
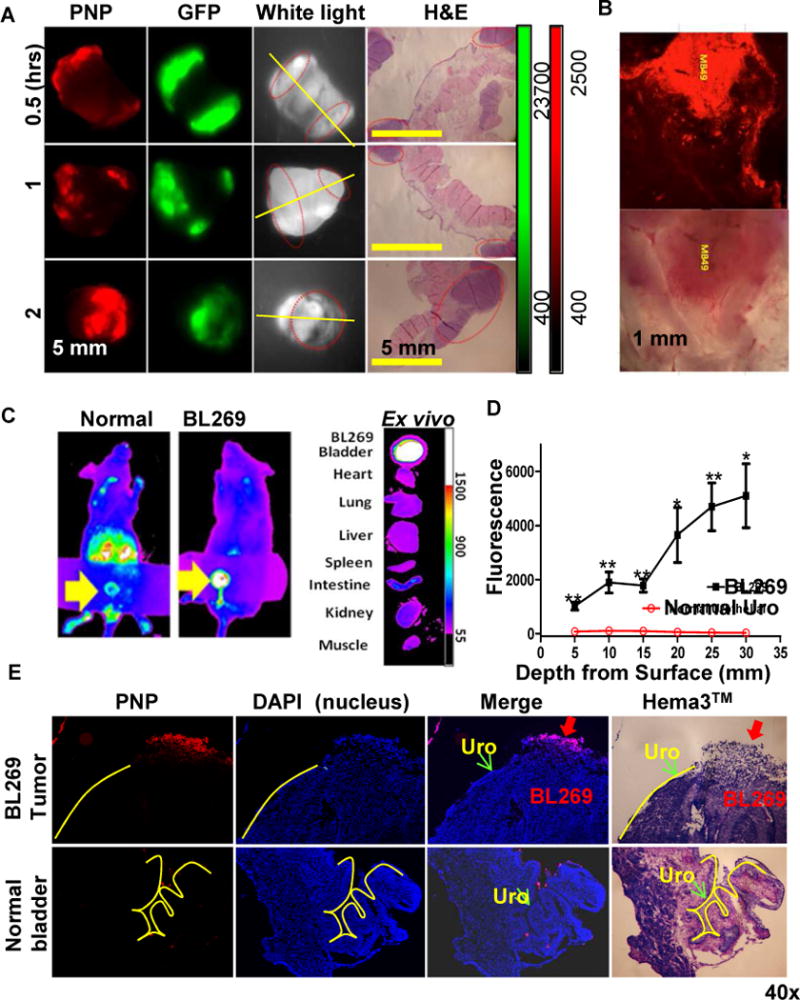
(A) PNPs mediated intravesical photodynamic diagnosis using Kodak imaging station in orthotopic mouse bladder cancer model. Mouse with established MB49-GFP-Luc bladder cancers were intravesically injected with 10 mg/ml PNPs (pyropheophorbide a: 2 mg/ml) using 26G blunt needle via urethra. After 2 hours, bladder and other major organs were harvested and imaged in the GFP (tumor cells) and NIRF channel (PNP uptake) using Kodak imaging station. Yellow line: cut line for histopathology; red circles: tumor locations. (B) Large scale 3-D confocal imaging (Leica) for PNP mediated photodynamic diagnosis in orthotopic mouse MB49 bladder cancer model. (C) Uptake of PNPs in an orthotopic PDX BL269 and other organs after intravesical administration of PNPs. (D) The penetration depth analysis between lumen exposed tumor sites and normal urothelium Cryosection was performed on bladder BL269 PDX samples. The fluorescence intensity was measured using Metamorph image analysis software at different spots and depth from lumen surface of tumor (such as red arrow) versus normal urothelial areas (such as green arrow). (p<0.01, t-test). (E) A representative cryosection showing selective uptake of PNPs by PDX bladder cancers (red arrow) but not normal urothelial cells (yellow lines).
