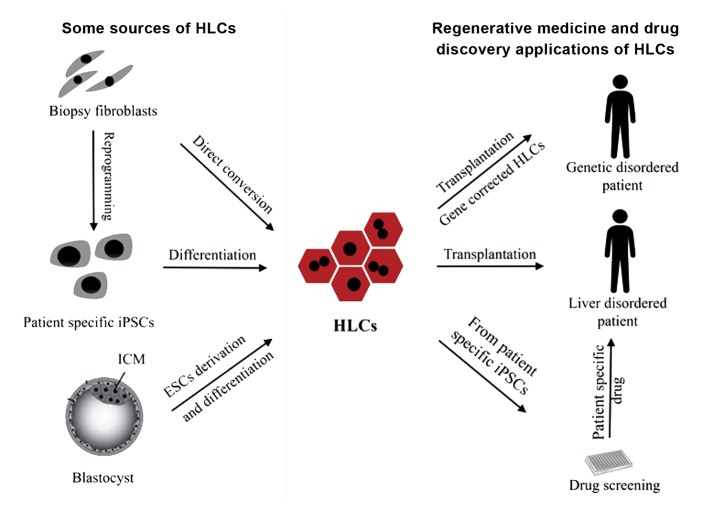
Fig.1.
Main sources of HLCs and their applications in regenerative medicine and drug discovery. Diagram of some sources of HLC (Left): biopsy derived fibroblasts from liver disease patient can directly be converted into HLCs, by overexpression of liver specific transcription factors (TFs). Patient specific iPSCs generated by overexpression of Yamanaka factors (Oct4, Sox2, Klf4 and c-Myc) can also be differentiated to HLCs for further applications. Embryonic stem cells from ICM of blastocyst are other sources of HLCs.
Diagram of some potential biomedical applications of HLC (Right): HLCs can be used for patients with end-stage liver disease. In addition, using iPSCs technology, monogenic disorders can be corrected in metabolic liver diseases at genome level and then healthy patient specific iPSC-derived HLCs could be a source for transplantation and decreasing signs of the disease. Drug screening after disease modeling, using patient specific iPSC-derived HLCs, to achieve new drugs for specific patients and individual drug administrations are another application of HLCs in the personalized medicine field.
HLCs; Hepatocyte-like cells and iPSCs; Induced pluripotent stem cells.