Figure 2. Depletion of API5 sensitizes cells to PFT‐induced apoptosis.
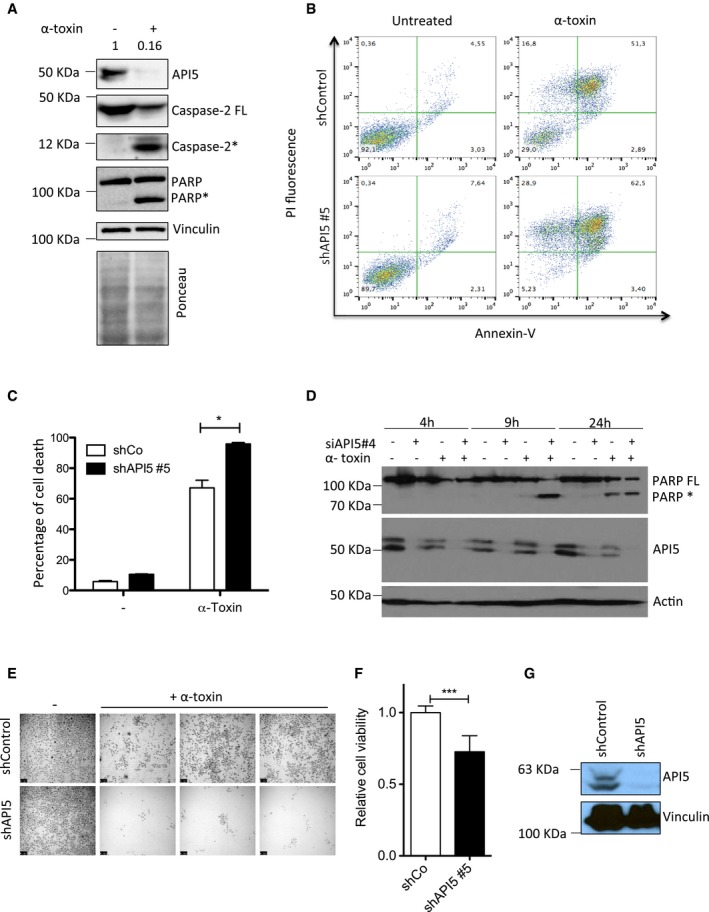
- API5 is degraded during PFT‐mediated apoptosis. HeLa cells were treated with α‐toxin (300 ng/ml for 24 h) and the presence of API5, caspase‐2, and PARP was tested by immunoblots. Ponceau‐stained membrane is presented below to verify the loading (* indicates processed caspase‐2 and PARP).
- API5 depletion sensitizes HeLa cells to PFT‐mediated apoptosis. ShControl and shAPI5 HeLa cells were treated with α‐toxin (600 ng/ml for 24 h), and the percentage of cell death was analysed by FACS. The Annexin V/PI staining pattern of control and toxin‐treated cells from a representative experiment is presented.
- Quantification of experiments presented in (B) (n = 3, Mann–Whitney test, *P‐value = 0.0286), error bars represent ±SD of the mean.
- HeLa cells were transfected with siRNAs (siControl or siAPI5#4) for 1 day prior to α‐toxin treatment. The cells were harvested for Western blot analysis at different time points (as indicated). FL: full length, *: processed PARP.
- HeLa cells were treated for 24 h with α‐toxin (300 ng/ml), and the dead cells were washed away. The surviving cells were allowed to replicate for 48 h to check for clonogenic survival. Shown are data from a representative experiment. Scale bar, 250 μm.
- For testing the viability of the cells, the crystal violet assay was performed on both control and shAPI5 treated with toxin and the surviving cells were quantified. The error bars represent the mean ± SD (n = 3, Mann–Whitney test, ***P < 0.0001).
- The efficiency of the shAPI5 was verified by Western blot and vinculin was employed as a loading control.
Source data are available online for this figure.
