Figure 5.
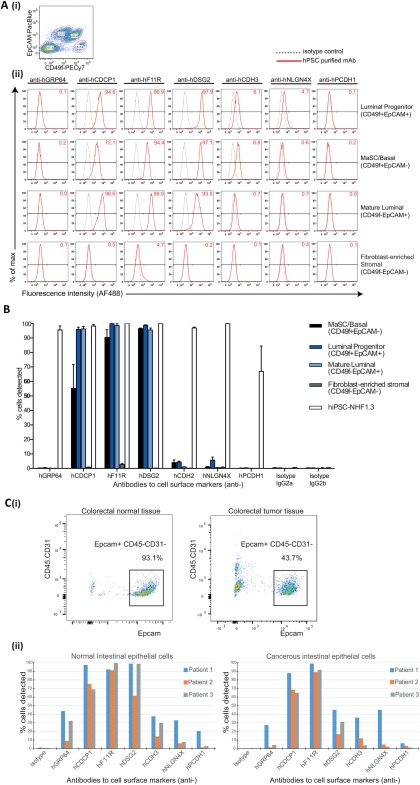
Expression of pluripotency‐associated antigens in human breast tissue and on normal and cancerous intestinal epithelial cells. (A): Human CD31−CD45−CD235a− cell populations isolated from mammary tissue were (i) fluorescence activated cell sorting (FACS)‐delineated using EpCAM and CD49f to resolve each of the four breast epithelial cell subsets:‐ luminal progenitor (CD49f+ EpCAM+), MaSC and basal (CD49f+ EpCAM−), mature luminal (CD49f−EpCAM+), and fibroblast‐enriched stromal (CD49f−EpCAM−); (ii) Representative flow histogram plots show the presence or absence of antigens detected by the purified monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) anti‐hGRP64, anti‐hCDCP1, anti‐hF11R, anti‐hDSG2, anti‐hCDH2, anti‐hNLGN4X, and anti‐hPCDH1 in these cell subsets, compared with isotype controls. (B): Bar graphs show the detection of pluripotency‐associated antigens for mammary cell subsets from four donor specimens as mean +/− SEM across two technical replicates compared with isotype controls and NHF1‐3 hiPS positive control cells. (C): (i) Human intestinal epithelial cells were isolated from normal and cancerous colorectal tissues by FACS selection for EpCAM+ CD31−CD45− cells. (ii) Bar graphs show the variation in detection of pluripotency‐associated antigens by the panel of mAbs (A‐B) on normal and cancerous intestinal epithelial cells from three patient donor samples compared with isotype controls. Abbreviation: hiPSCs, human iPS cells.
