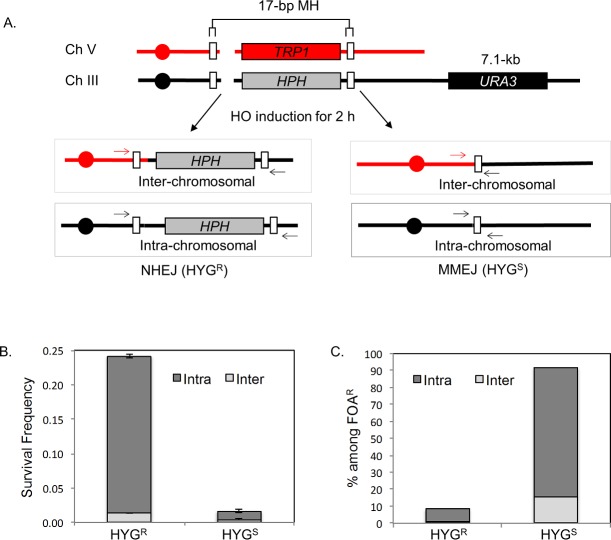
Fig 5. MH-induced mutagenesis at chromosomal translocation breakpoints.
A. Schematics illustrating the yeast strain that produces intra- or inter-chromosomal MMEJ or NHEJ upon HO expression. The strain has two HO recognition sites, one on Chromosome III and the other on Chromosome V. White boxes denote the location of 17-bp MH near the break site. HPH and TRP1 markers are shown. Four possible repair outcomes in this strain after DSB induction based on hygromycin sensitivity (HYGs) or resistance (HYGr) and the types of chromosomal joints are shown. The formation of chromosomal translocations was determined by PCR across the HO cleavage sites using primers annealed to two different chromosomes (arrows). B. Types of repair events among survivors. Survival frequency is calculated by dividing the number of survivors by the number of cells plated. A DSB was induced in the strain for 2 h by incubation in YEP-galactose and cells were plated on YEP-dextrose after serial dilution. The percentage of intra- and inter-chromosomal repair events was determined by PCR analysis of 100 colonies from each survivor. The results are the average of three independent experiments ± s.d. C. Types of FOAR survivors after HO expression. The percentage of intra- vs inter-chromosomal repair events and the status of the hygromycin resistance gene are plotted. A DSB was induced for 2 h and cells were plated onto YEP-dextrose and subsequently replica plated onto 5-Fluoroorotic Acid (5-FOA) plates. 100 colonies from each experiment were analyzed by PCR to detect intra-chromosomal or inter-chromosomal repair products. The results are the average of three independent experiments.