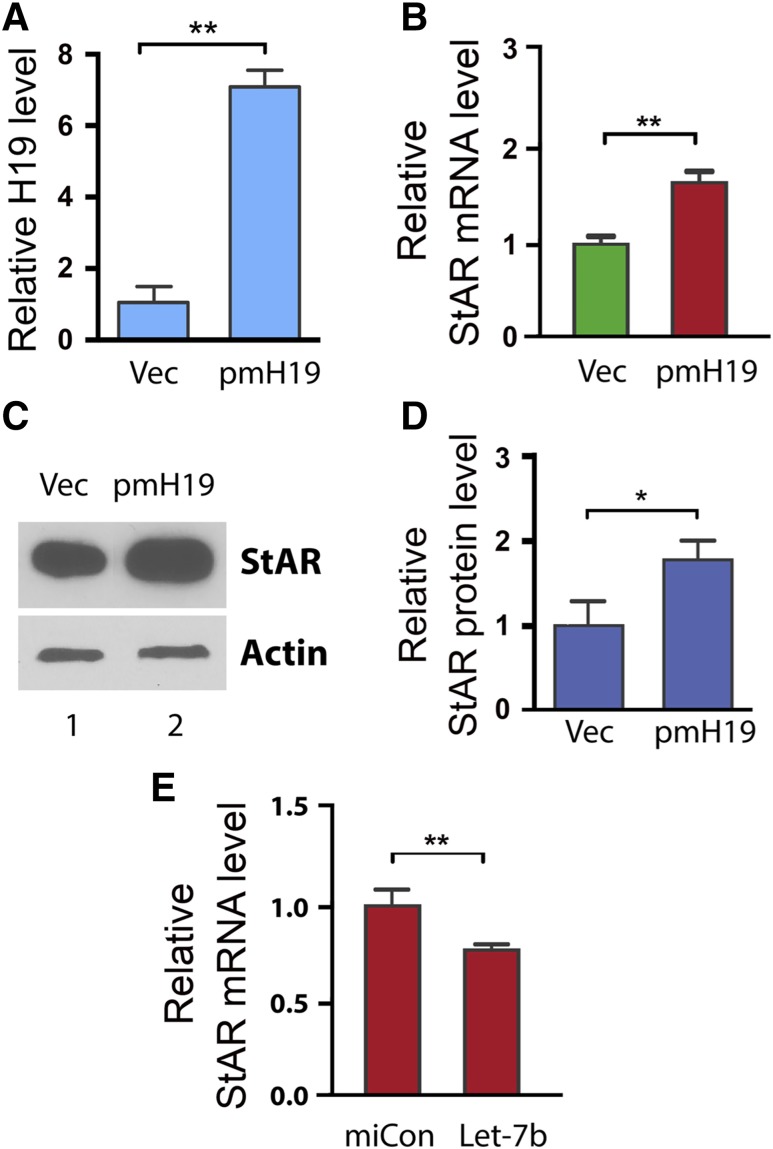
Figure 4.
H19-mediated regulation of StAR is conserved in other steroidogenic cells. To test whether the H19-mediated regulation of StAR is conserved, we examined the effect of H19 overexpression on StAR expression in the mouse Leydig cell line MLTC-1. (A, B) MTLC-1 cells were transfected with empty vector (Vec) or with pH19. RNAs were isolated 48 h post-transfection and analyzed by qRT-PCR for H19 and StAR expression. Numbers are mean ± SD (n = 3). **P < 0.01. (C, D) StAR protein was extracted and analyzed by Western blotting. β-Tubulin was used as a loading control. Results are representative of 3 independent transfection experiments. Western blot quantifications (D) were performed using ImageJ. Numbers are mean ± SD (n = 3). *P < 0.05. (E) To confirm the functionality of the predicted let-7b binding site in the mouse StAR mRNA, we tested the effect of let-7b on inhibition of endogenous StAR expression. Thus, let-7b (or miRNA negative control miCon) was transfected into MLTC-1 cells. RNAs were extracted 12 h later, and StAR mRNA levels were determined by qRT-PCR. Let-7 transfection led to decreased StAR expression, supporting StAR being a target of let-7b inhibition in the mouse cells.