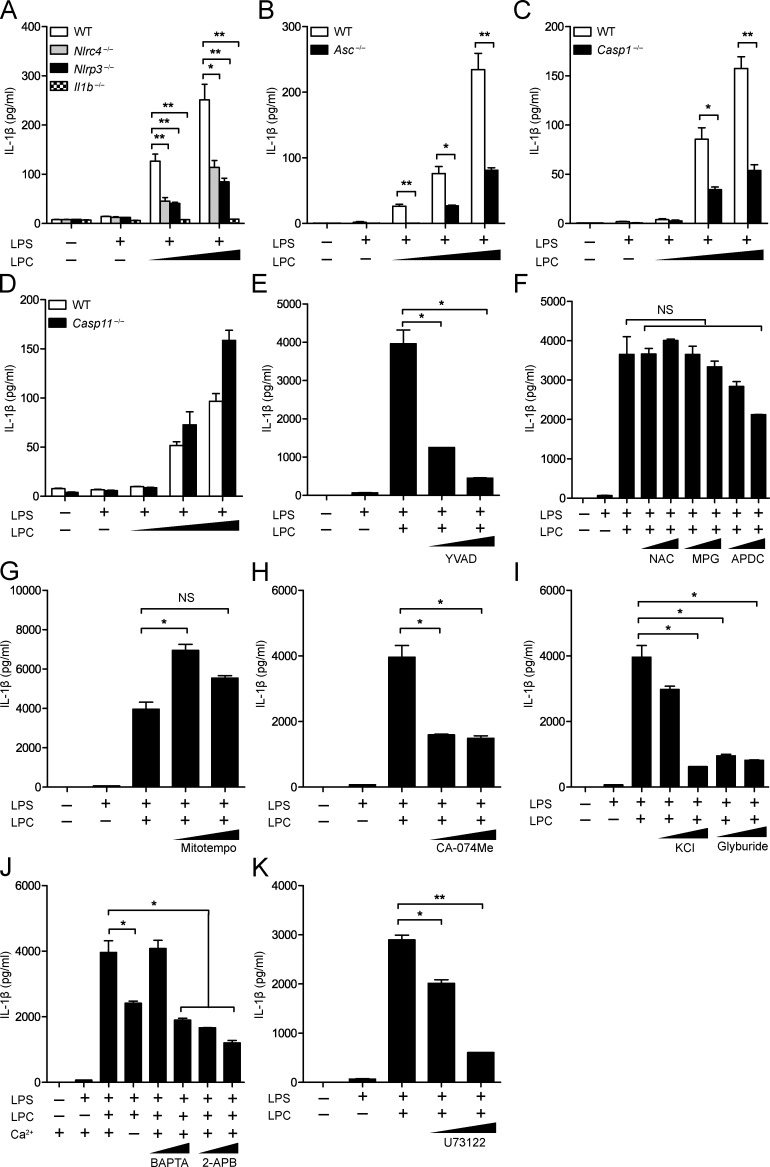
Figure 1.
The inflammasome mediates LPC-induced IL-1β secretion in mouse BMDMs. (A–D) WT, Nlrc4−/−, Nlrp3−/−, Il1b−/− (A), Asc−/− (B), Casp1−/− (C), and Casp11−/− (D) BMDMs were LPS primed (100 ng/ml) overnight before LPC stimulation at concentrations of 25, 50, and 100 µM for 1 h before IL-1β was collected from supernatants for analysis by ELISA. (E–K) BMDMs were LPS primed (200 ng/ml) for 3 h before stimulation with 50 µM LPC in the presence or absence of the caspase-1 inhibitor YVAD (10 and 50 µM; E); the ROS inhibitors NAC (5 and 25 mM), MPG (1 and 2.5 mM), and APDC (10 and 50 µM; F); the mitochondrial ROS inhibitor Mitotempo (100 and 500 µM; G); the cathepsin B inhibitor (CA-074Me; 10 and 20 µM; H); the potassium efflux inhibitors KCl (50 and 100 mM) and glyburide (100 and 200 µM; I); or the calcium inhibitors BAPTA (10 and 20 µM), 2-APB (20 and 100 µM; J), and U73122 (2 and 10 µM; K). Then, IL-1β was collected from supernatants for analysis by ELISA. Each control and experimental condition was performed in triplicate. All data are representative of at least two independent experiments. Results are displayed as the mean ± SEM. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; unpaired Student's t test.