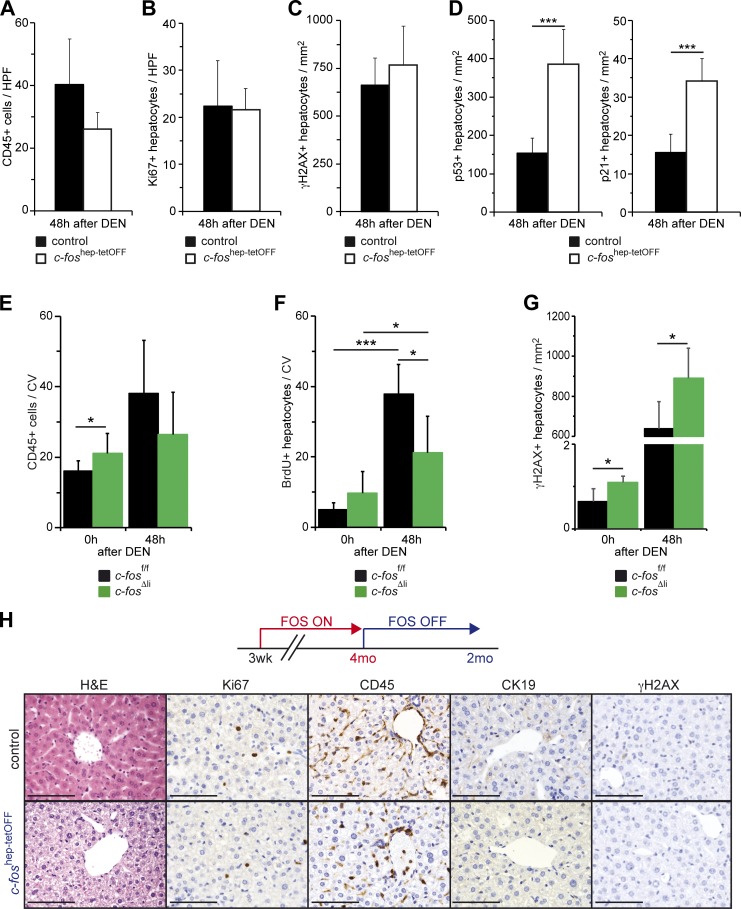
Figure 4.
c-Fos–dependent early carcinogenic events and phenotype reversibility. (A–D) Quantification of CD45-positive cells (A; n = 5/5) and Ki67-positive (B; n = 5/5), γH2AX-positive (C; n = 4/5), and p53-positive (n = 4/5) and p21-positive (D; n = 4/5) hepatocytes in liver sections from 8-wk-old c-foshep-tetOFF and control mice 48 h after DEN. (E–G) Quantification of CD45-positive (E; n = 8; 6/8; 5) and BrdU-positive (F; n = 4; 7/3; 6) cells around the central vein (CV) and γH2AX-positive hepatocytes (G; n = 4/5) in liver sections from 8-wk-old c-fosΔli and control mice untreated (0) and 48 h after DEN. (A–G) Plots represent mean ± SD; *, P ≤ 0.05; ***, P ≤ 0.001 by Student’s t test. (H) Ectopic expression of c-Fos was allowed during 4 mo and then stopped by administration of doxycycline. Representative liver histology (H&E) and IHC (Ki67, CD45, CK19, and γH2AX) from c-foshep-tetOFF and controls 2 mo after switching off c-Fos expression. Bars, 100 µm.