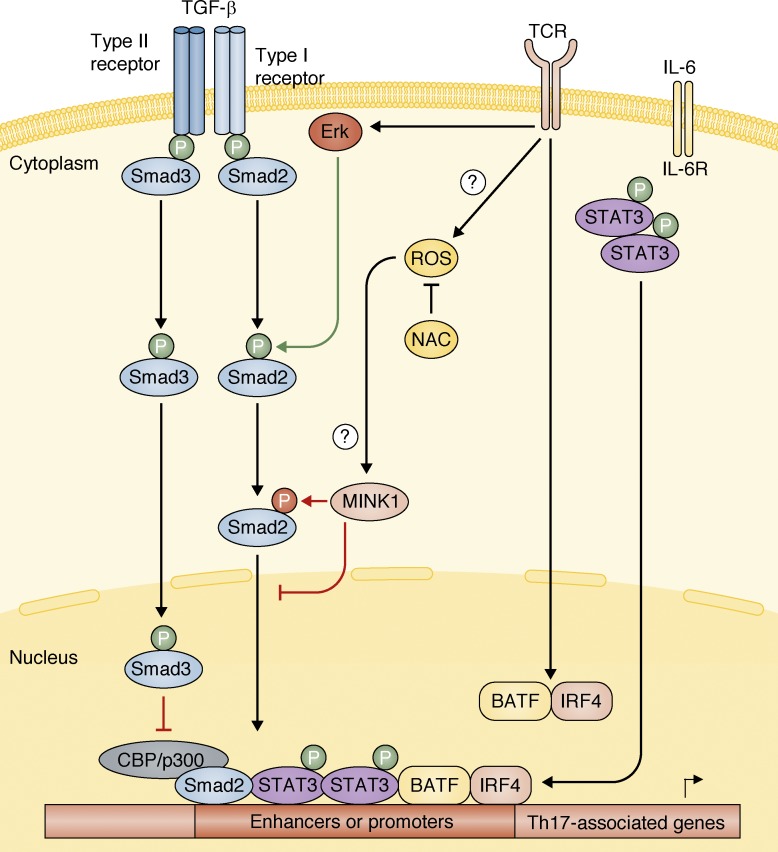
Mink1 inhibits Smad2-mediated Th17 cell induction. Upon TCR and co-stimulatory molecules signals, ROS are induced, which in turn can lead to the activation of the kinase Mink1. Also, the pioneering transcription factors BATF and IRF4 are activated upon TCR/co-stimulation signals, which induce chromatin remodeling at Th17-associated genes, allowing chromatin to be accessible to other transcription factors. TGF-β signaling induces activation of Smad2 and Smad3. Smad2 is required for proper Th17 cell generation (Malhotra et al., 2010; Martinez et al., 2010; Yoon et al., 2015), whereas Smad3 inhibits the generation of Th17 cells (Martinez et al., 2009). Previous studies have shown that Smad2, phosphorylated by Erk upon TCR and TGF-β stimulation, cooperates with Stat3 in the induction of Th17 cells (Yoon et al., 2015). In this issue of JEM, Fu et al. (2017) now demonstrate that the activation of Mink1 by ROS species, which can be blocked by NAC treatment, leads to an inhibitory phosphorylation of Smad2 in T324 residue, preventing its nuclear localization and therefore induction of Th17-associted genes.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.