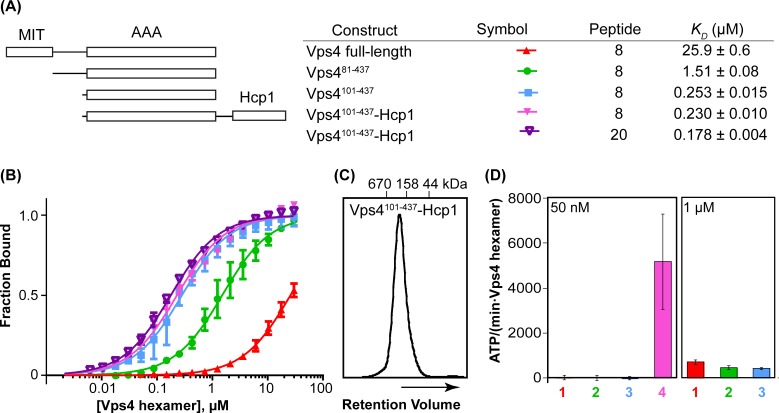
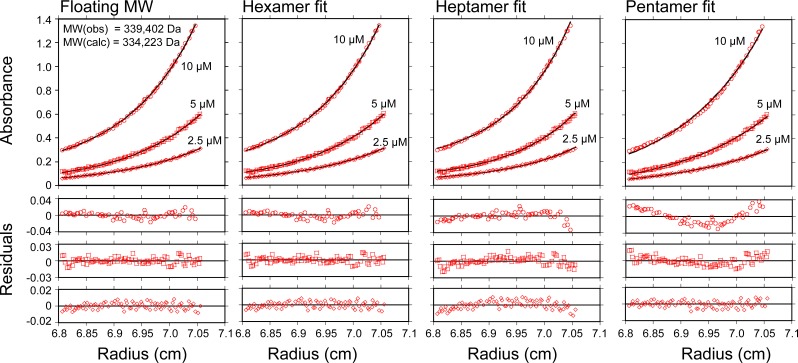
Figure 1. Vps4101-437-Hcp1 is an active hexamer.
(A) Vps4 constructs and peptide-binding affinities assayed by fluorescence polarization. Peptide ‘20’ is a Vps2-derived 20-residue peptide C identified earlier (Han et al., 2015). Peptide ‘8’ is an 8-residue fragment (DEIVNKVL) of peptide ‘20’ that retains essentially full binding affinity. The relatively weak binding of full-length Vps4 reflects autoinhibition mediated by the MIT domains (Han et al., 2015). (B) Fluorescence polarization isotherms corresponding to values in panel A. Means and standard deviations are from four independent experiments. (C) Gel filtration of Vps4101-437-Hcp1 on a Superdex 200 column in 25 mM Tris/HCl pH 7.4, 100 mM NaCl and 1 mM DTT. The protein elutes as a symmetric peak with an apparent molecular mass of 290 kDa, in good agreement with the calculated molecular mass of a hexamer (330 kDa). (D) ATPase activities for Vps4 constructs: 1, Vps4 full-length; 2, Vps481-437; 3, Vps4101-437; 4, Vps4101-437-Hcp1. Vps4 subunit concentrations are indicated. Means and standard deviations from at least three independent measurements.
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.7554/eLife.24487.003