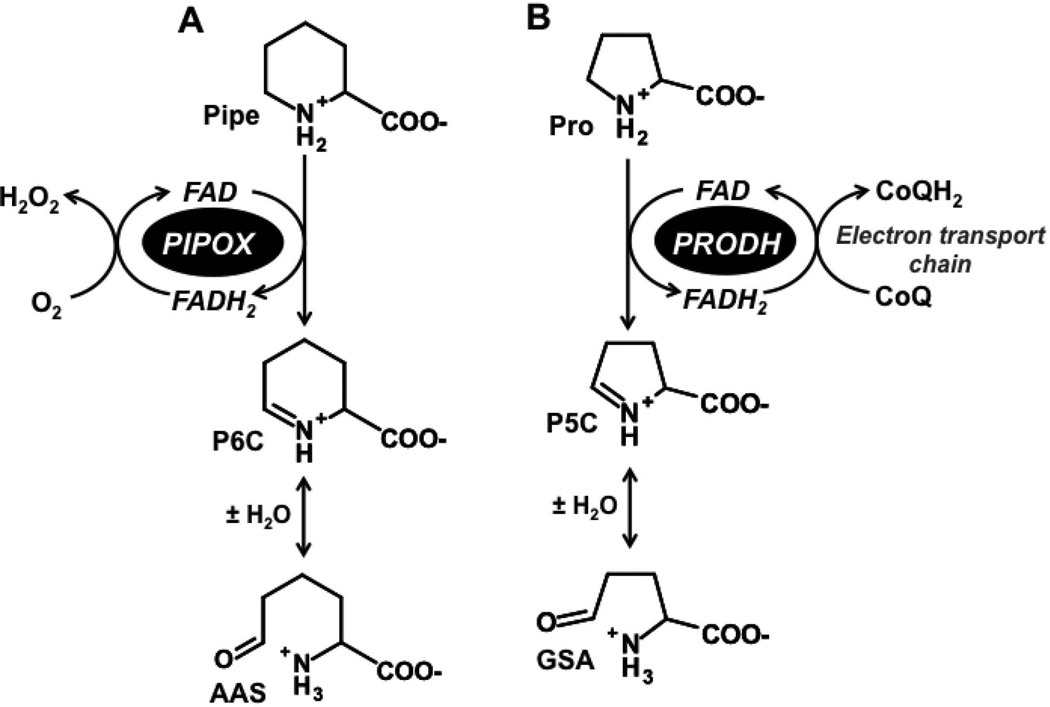
Figure. 1. Reactions catalyzed by pipecolate oxidase and proline dehydrogenase.
(A) Pipecolate oxidase (PIPOX) catalyzes the oxidation of L-pipecolate (Pipe) to Δ1-piperideine-6-carboxylate (P6C). P6C spontaneously hydrolyzes to form α-aminoadipic semialdehyde (AAS). (B) In an analogous reaction, proline dehydrogenase (PRODH) catalyzes the oxidation of L-proline (Pro) to Δ1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate (P5C), which spontaneously hydrolyzes to glutamate γ-semialdehyde (GSA).