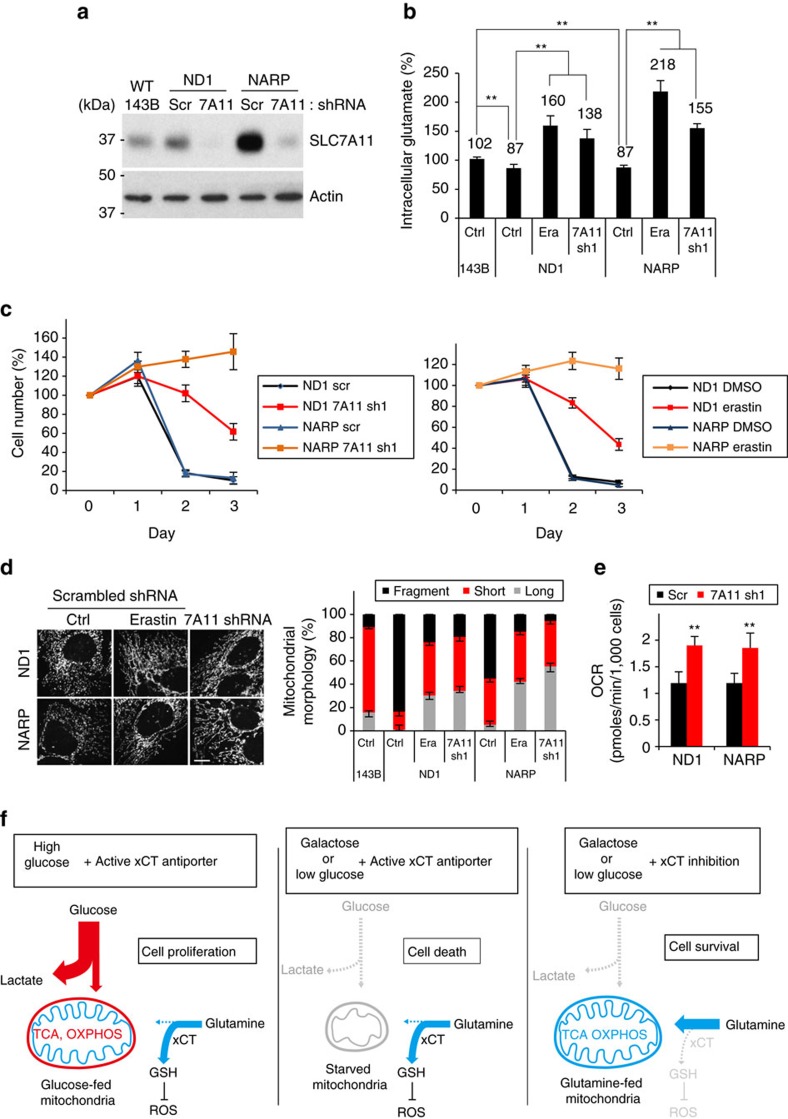
Figure 6. Inhibition system xc− enhances viability and mitochondrial function of cybrid cells harbouring mtDNA mutations.
(a) Western blot of SLC7A11 levels in 143B and isogenic mtDNA-mutant ND1 and NARP cells. (b–e) Analysis of SLC7A11 knockdown or erastin (Era)-treated (5 μM) ND1 and NARP cells cultured in the presence of 10 mM galactose and 2 mM glutamine. (b) Quantification of intracellular glutamate at 24 h after galactose culture. Data represent the means±s.d. (n=4); ** P<0.01; unpaired Student's t-test. (c) Cell viability in galactose medium for 3 days. Data represent the means±s.d. (n=4). (d) Representative images and quantification of mitochondrial morphology at 24 h after galactose culture. Data represent the means±s.d. (n=3). Scale bar, 10 μm. (e) Oxygen consumption was determined at 24 h after galactose culture. Data represent the means±s.d. (n=5); **P<0.01; unpaired Student's t-test. (f) Model for the dual effects of the xCT antiporter. The xCT antiporter diverts glutamine metabolism from the TCA cycle into GSH synthesis, which is important for antioxidant function. Under certain cellular conditions, excessive diversion of glutamine from the TCA cycle is detrimental (middle panel) and therefore inhibition of the antiporter improves survival (right panel).