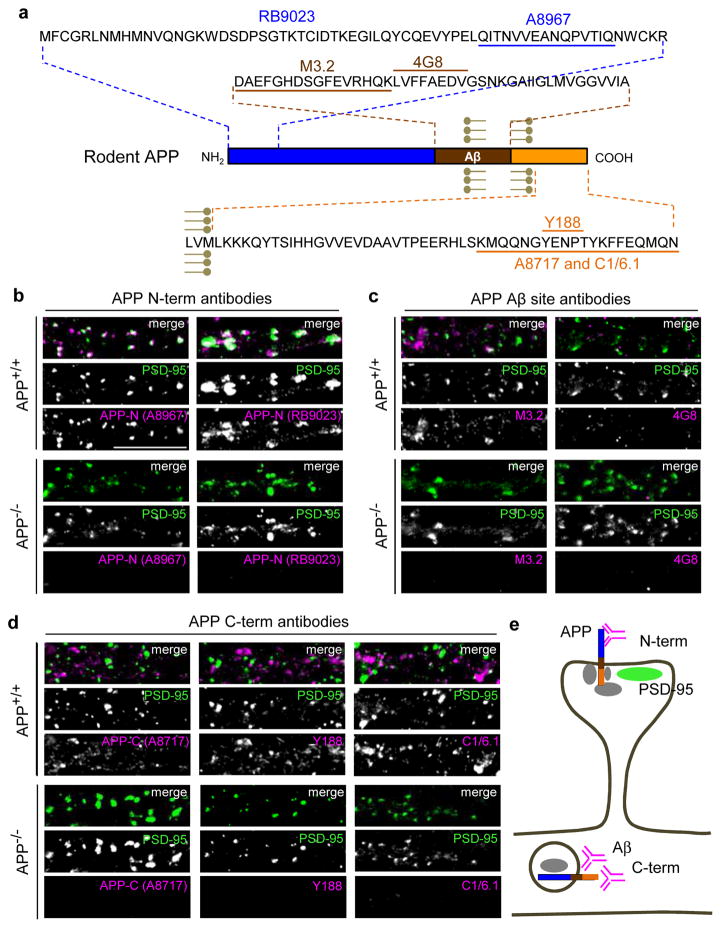
Fig. 1. APP localized to excitatory synapses is detected exclusively by N-terminal directed antibodies.
(a) Schematic of APP sequence showing epitopes of antibodies used in immunostaining (epitope for N-terminal RB9023 has not been reported). (b–d) Immunocytochemistry of dendrites from cultured hippocampal neurons (14 days in vitro (DIV)) of wild-type (APP+/+, WT C57BL/6) or APP knockout (APP−/−, KO) mouse using N-terminal, Aβ site, and C-terminal directed antibodies as indicated (magenta), co-labeled with excitatory marker PSD-95 (green) (co-localization shows as white in merge) under permeabilizing conditions. Note complete absence of APP signal in knockout neurons. Scale bars, 10 μm. (e) Hypothetical interpretation of results. Synaptic APP (co-localizing with PSD-95, green), is recognized only by N-terminal antibodies (C-terminal and Aβ site antibodies are masked, possibly by APP scaffold proteins (gray)). APP in dendrites is recognized by C-terminal and Aβ site antibodies only (N-terminal antibodies are blocked, possibly by vesicular membranes). It is unknown if Aβ site and C-terminal antibodies recognize the same subpopulation of full-length APP; these antibodies may also visualize APP processing fragments. APP at other locations such as presynaptic terminals cannot be assessed with these antibodies.