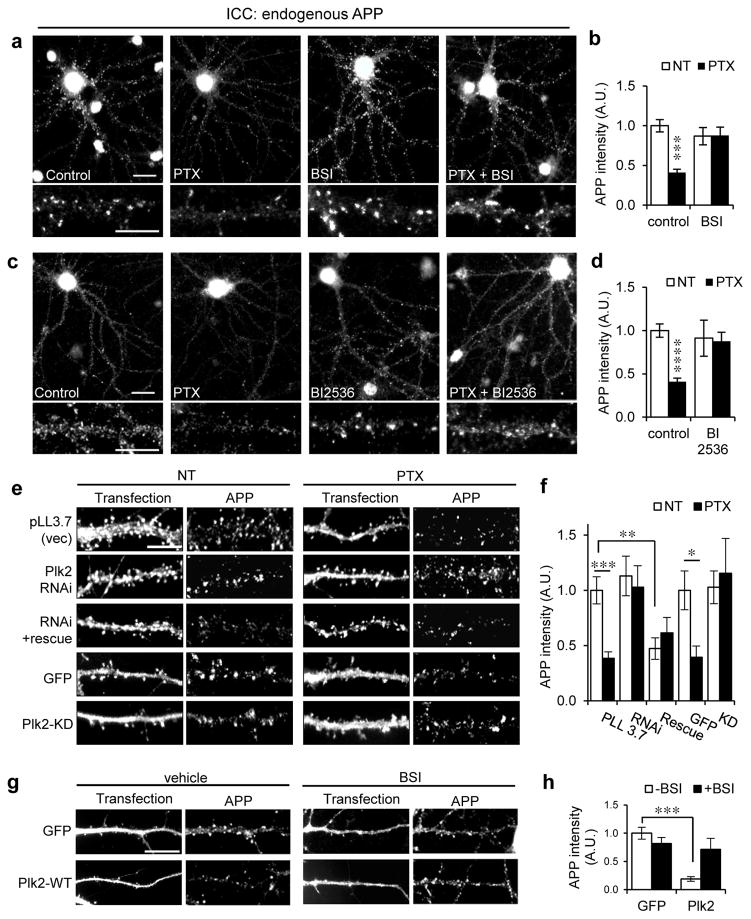
Fig. 2. Activity-dependent synaptic APP loss requires β-secretase and Plk2.
(a, c) Hippocampal neurons (day in vitro (DIV) 20–24) were treated with picrotoxin (PTX, 25 μM, 20 h) or vehicle and co-treated with β-secretase inhibitor (BSI II, 1 μM), Plk inhibitor BI2536 (50 nM), or vehicle as indicated, then immunolabeled for endogenous rat APP with polyclonal APP-N antibodies. Representative dendrites shown below. (b) Quantification of a (n=44 neurons for NT, 38 for PTX, 16 for BSI, 18 for PTX+BSI). (d) Quantification of c (n=34 neurons for NT, 26 for PTX, 10 for BI2536, 9 for PTX+BI2536). (e) Neurons were transfected with empty vector (pLL3.7) or constructs as indicated for 3 days and treated with PTX (25 μM, 20 h) or vehicle (NT), then immunolabeled for endogenous APP and either transfected GFP or Plk2 as indicated. (f) Quantification of e (n=16 neurons for vector, 9 for vector+PTX, 10 for shRNA, 18 for shRNA+PTX, 7 for Plk2 shRNA+rescue, 7 for Plk2 shRNA+rescue+PTX, 11 for GFP NT, 9 for GFP+PTX, 7 for Plk2 KD, 7 for Plk2 KD+PTX). (g) Neurons were transfected with GFP or Plk2-WT, treated with BSI II (1 μM, 20 h) or vehicle (DMSO), and immunolabeled for GFP or Plk2 and APP N-terminus. (h) Quantification of g (n=32 neurons for GFP+vehicle, 16 for GFP+BSI, 11 for Plk2+vehicle, 9 for Plk2+BSI). ****P<0.0001; ***P<0.001; **P<0.01, *P<0.05; ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc test. Data are means±SEM. Experiments were performed in at least duplicate. Scale bars, 10 μm.