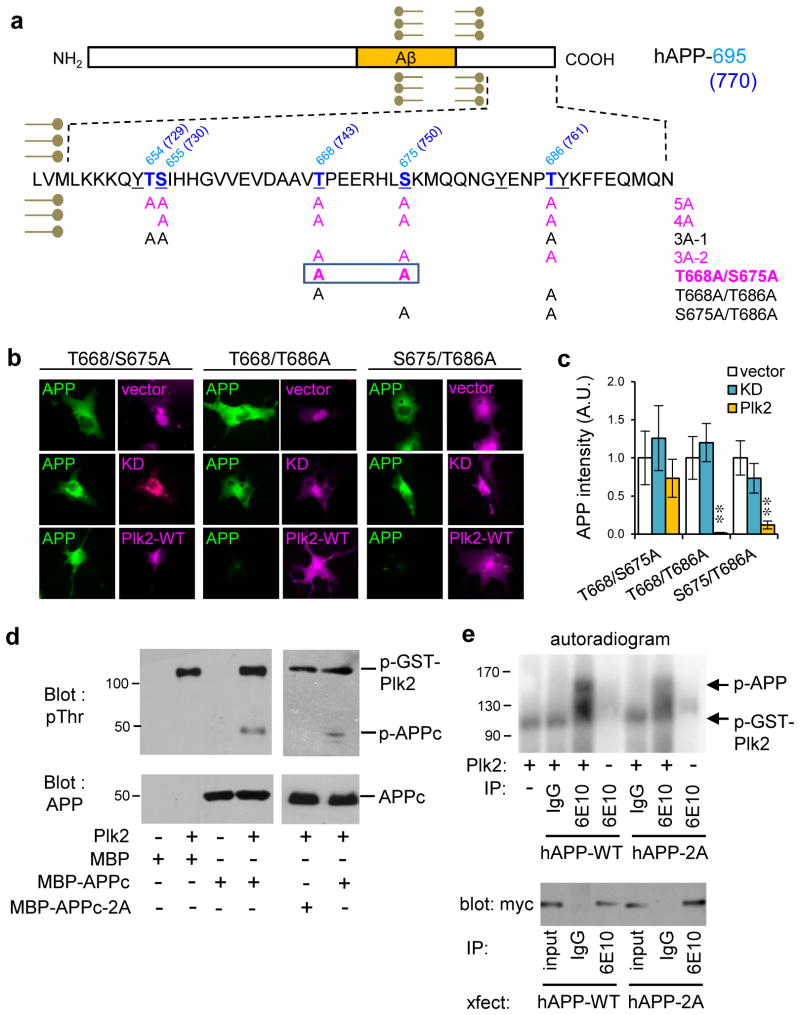
Fig. 5. Direct phosphorylation of APP by Plk2.
(a) APP intracellular domain showing mutants in the study; amino acid numbering given for both hAPP-695 and hAPP-770 (in parentheses). Bold blue, serine/threonine residues. Underline, residues hyperphosphorylated in AD brain. Magenta, mutants insensitive to Plk2. (b) Myc-tagged APP double mutants T668/S675A, T668/T686A or S675/T686A were co-transfected with HA-vector, HA-Plk2-KD or HA-Plk2-WT in COS-7 cells and labeled with myc antibody for APP (green) and HA antibody for vector or Plk2 (magenta). (c) Quantification of b (T668/S675A: n=8 cells for vector, 9 for Plk2-KD, 6 for Plk2-WT; T668/T686A: n=8 cells for vector, 8 for Plk2-KD, 6 for Plk2-WT; S675/T686A: n=5 for vector, 5 for Plk2-KD, 7 for Plk2-WT); **P<0.01, ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc test; data are means±SEM. (d) In vitro kinase assay using purified MBP, MBP-APPc, or MBP-APPc-2A with or without purified recombinant full-length GST-Plk2 protein. Reactions were immunoblotted using phosphothreonine and human/rodent-specific APP C-terminus antibodies. (e) (Top) Autoradiogram of in vitro kinase assays using full-length (FL) myc-hAPP-WT or myc-hAPP-2A immunopurified from COS-7 cells with antibody 6E10, or nonimmune IgG, and incubated in the presence or absence of GST-Plk2. (Bottom) Representative myc western blots of immunopurified myc-hAPP-WT and myc-hAPP-2A from COS-7 for in vitro kinase assay. Recovery of hAPP-2A was consistently greater than hAPP-WT with 6E10 antibody, but no recovery was obtained with nonimmune mouse IgG. Molecular weights in kDa. Experiments were performed in at least duplicate. Cropped blots are displayed for clear and concise presentation. Full blots are shown in Supplementary Fig. 10.