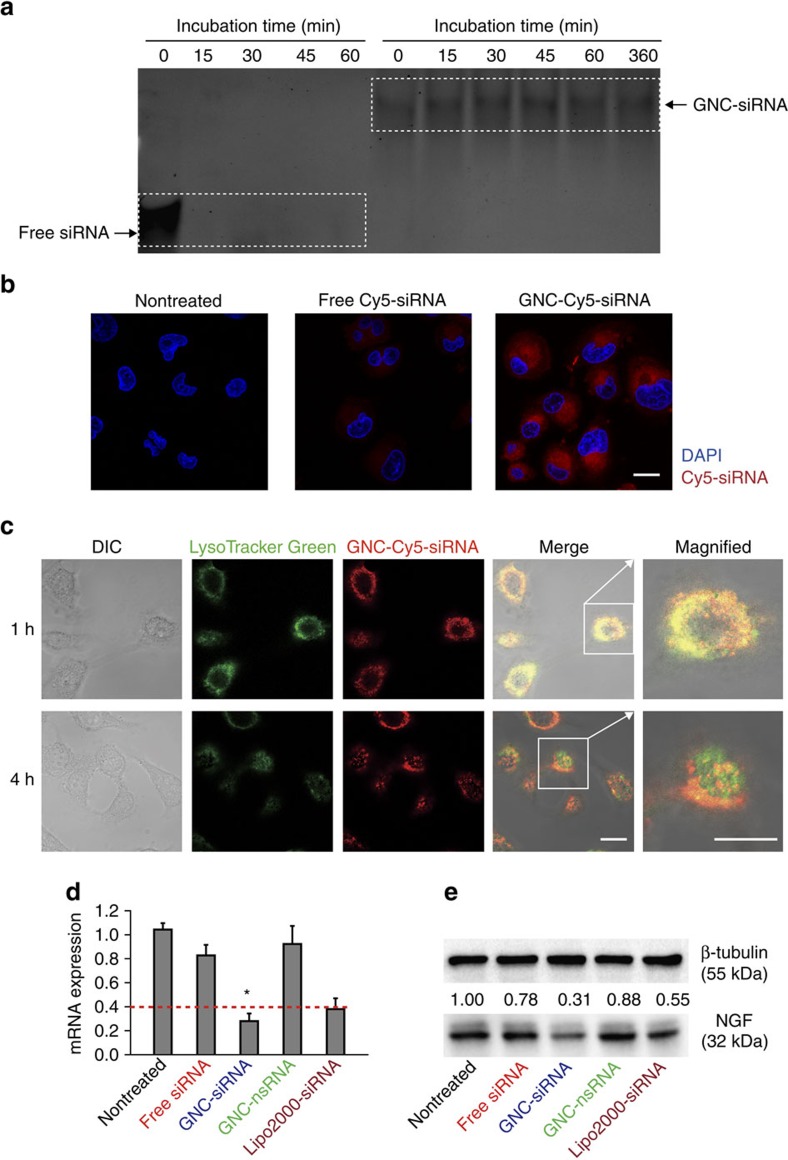
Figure 3. Characterization of GNC–siRNA in vitro.
(a) Protection of siRNA against serum nucleases. Free siRNA and GNC–siRNA (100 nM siRNA) were incubated within 10% serum for multiple time points, and analysed by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. (b) Cellular uptake of free siRNA and GNC–siRNA into Panc-1 cells. siRNA was labelled with Cy5 dye (Cy5-siRNA), the Panc-1 cells were incubated with various Cy5-siRNA formulations for 1 h and observed by confocal microscope with a 633 nm laser excitation. Nuclei were counterstained with 4,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI; blue). Scale bars, 20 μm. (c) Lysosomal escape of GNC–siRNA in Panc-1 cells. The lysosomes of cells were stained with LysoTracker Green for 1 h, and the Panc-1 cells were treated with GNC–Cy5-siRNA for 1 h. The cells were observed by confocal microscope over different time points. Scale bars, 20 μm. (d) Expression level of NGF mRNA in Panc-1 cells analysed by RT–PCR, the dotted line referred to the expression level of NGF mRNA in Panc-1 cells transfected with commercially available Lipofectamine 2000 transfection agent (Lipo2000-siRNA), which served as a positive control. Mean±s.d. (n=3). *P<0.01 compared with the nontreated control; Student's t-test. (e) Expression level of NGF protein in Panc-1 cells evaluated by western blotting. GNC binding with nsRNA was labelled as GNC–nsRNA and served as control siRNA.