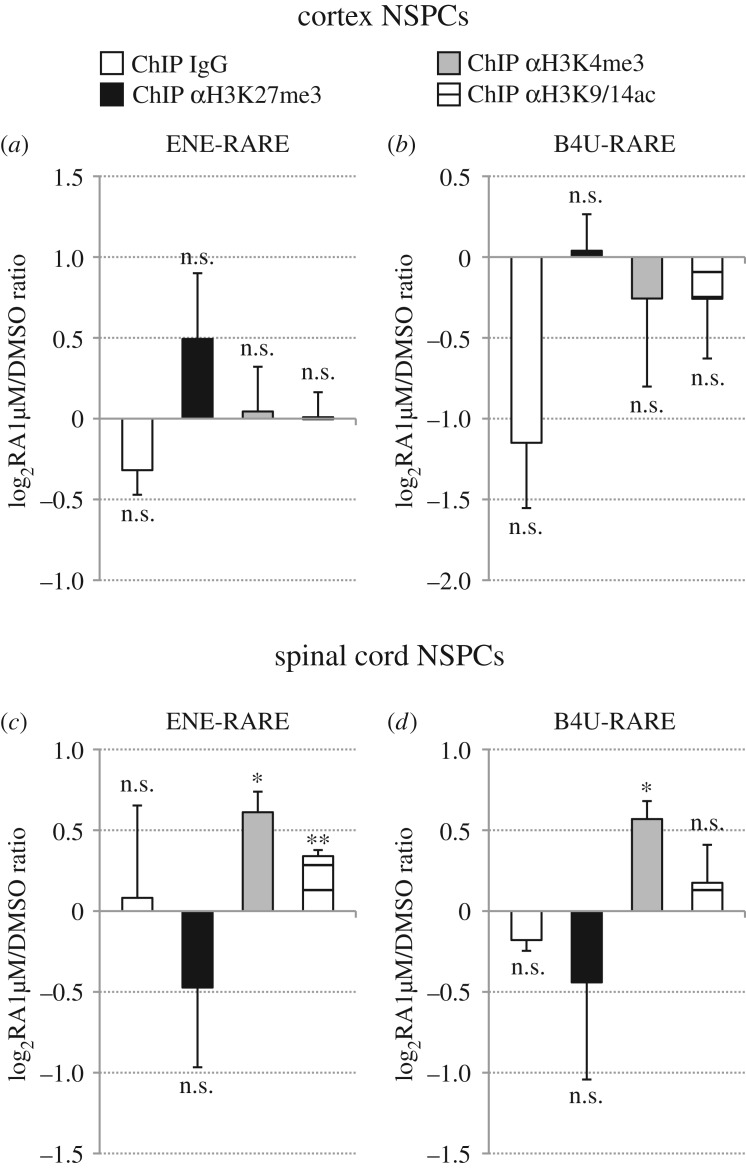
Figure 5.
Retinoid signalling promotes H3K4me3 and H3K9/14ac deposition in Hoxb RAREs of spinal cord NSPCs, but does not alter H3K4me3, H3K27me3 and H3K9/14ac levels in Hoxb RAREs of cortex NSPCs. (a–f) Real-time PCR quantification of ChIP assays in cortex (a,b) and spinal cord (c,d) NSPCs that were treated with either DMSO or 1 µM RA for 48 h, using control (IgG), anti-H3K27me3 (αH3K27me3), anti-H3K4me3 (αH3K4me3) or anti-H3K9/14ac (αH3K9/14ac) antibodies. Primer pairs used for real-time PCR target ENE-RARE (a,c) or B4U-RARE (b,d). A significant increase in H3K4me3 and H3K9/K14ac levels is detectable in RA-treated spinal cord NSPCs relative to DMSO-treated cultures, while H3K27me3 levels are not significantly affected. H3K4me3, H3K27me3 and H3K9/K14ac levels do not show significant differences following RA treatments of cortex NSPCs. No significant changes between RA-treated and DMSO-treated samples are detectable following control ChIP (ChIP IgG). Results are shown as the mean of the log2-transformed ratio between RA-treated and DMSO-treated NSPCs in three to four biological replicates, following normalization to the reference amplicon. Error bars show s.e.m. *p ≤ 0.05; **p < 0.01; n.s., non-significant (p > 0.05) according to a two-tailed Student's t-test performed between RA-treated and DMSO-treated samples.