Fig. 1.
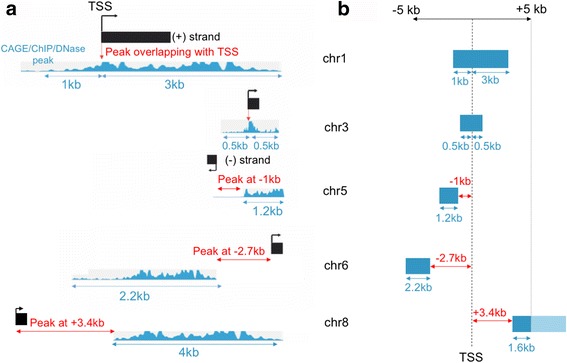
The closest CAGE-seq/ChIP-seq/DNase-seq peak to each TSS is rapidly retrieved using a binary search. a The process of finding the closest CAGE peak takes into account the strand information supplied by the user (ChIP-seq and DNase-seq data are unstranded). If a TSS is located on the positive DNA strand (TSSs on chromosomes 1, 3, 6 and 8), peaks with a genomic coordinate greater than the TSS are considered downstream (=positive distance) of the genomic feature. If a TSS is located on the negative DNA strand (third TSS on chromosome 5), peaks with a genomic coordinate greater than the TSS are considered upstream (=negative distance) of the genomic feature. Peak widths and overall peak enrichment for each region (signalValue for ChIP-seq and DNase-seq data; tpm expression values for CAGE-seq) are simultaneously retrieved. b Once the distances to the closest peaks have been retrieved they are ordered and placed on top of a vertical axis representing the TSS. Since the Zipper plot is visualized (by default) in a 5 kb window, peaks that are wider than 5 kb or are further away from the TSS will not appear (i.e. TSS on chromosome 8; darker region will appear whereas the faded region exists but it is not displayed)
