Fig. 2.
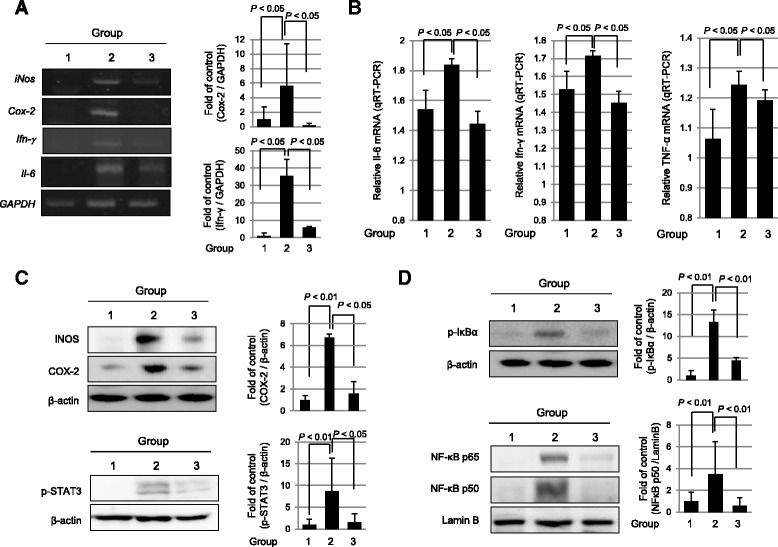
hPDSCs inhibit the expression of inflammation-associated factors in irradiated intestine. a RT-PCR for the proof of inflammatory cytokines in the radiation injury. Data showed RT-PCR results for checking the expression of iNOS, COX-2 and IFNγ. b The expression of inflammatory markers IL6, IFNγ and TNF-α were measured by real-time PCR. c The expression of iNOS, COX2, phosphorylated STAT3 and β-actin (as loading control) in protein extracts of each according group measured with Western blotting. d Nuclear extracts were performed by immunoblotting with antibodies of p65, p50, and lamin B. Cytoplasm extracts were anti-phosphorylated IκBα and β-actin. Results are representative of three independent samples. Western blotting analysis was performed with indicated antibodies. All bars represent the mean and SD of triplicate values respectively. COX-2 cyclooxygenase-2, IFN-γ interferon gamma, IκBα inhibitor of kappa B, IL-6 interleukin 6, iNOS nitric oxide synthase, IR ionizing radiation, NF-κB nuclear factor-κB, p-STAT3 phosphorylated signal transducer and activator of transcription 3, TNF-α tumor necrosis factor alpha
