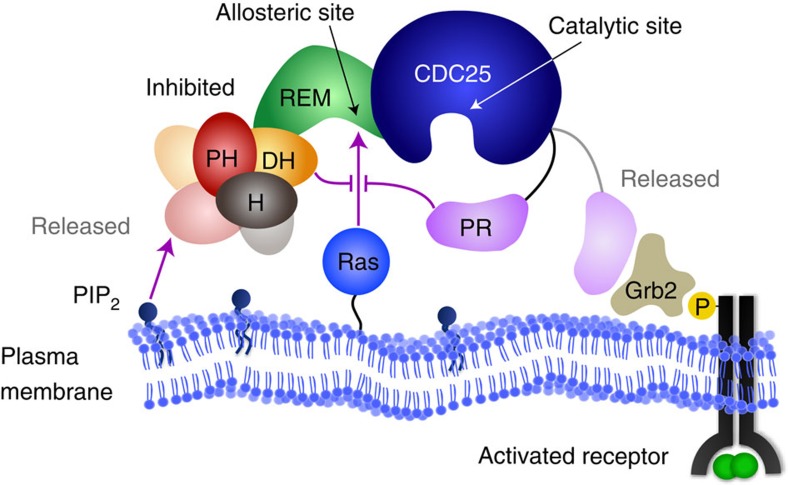
Figure 7. The complete autoinhibition of SOS requires allosteric inhibitory modes of both the N- and C-terminal regulatory modules.
The regulatory modules control kinetic rates of membrane recruitment and allosteric activation of SOS. The inhibitory functions of N- and C-terminal regulatory modules are independent of each other. Distinctive membrane interactions such as with lipids or activated receptors may release each inhibitory conformation and modulate allosteric activation probability of SOS in cells.