Fig. 4. TMEM24 harbors a phosphatidylinositol (PI)–binding SMP module.
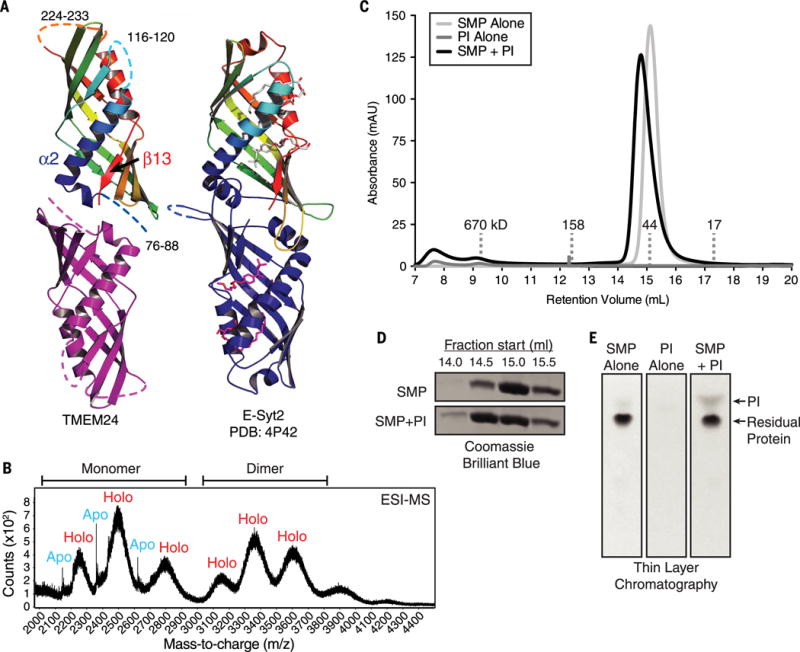
(A) TMEM24 (76 to 260) adopts an SMP domain fold. TMEM24 SMP domain is modeled as a dimer by analogy to the E-Syt2 SMP domains (at right). Disordered segments are represented as dashed lines. TMEM24 helix α2 and strand β13 move closer compared with the corresponding helix and strand in the liganded E-Syt2 structure. Four lipid molecules bound by E-Syt2 dimer are indicated. (B) Native electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (ESI-MS) analysis of TMEM24 SMP domain purified from Expi293 cells indicates dimerization, with masses consistent with one phospholipid molecule bound per monomer. Whereas the monomeric fraction exists in both apo and holo form, the dimeric fraction is mostly complexed with lipid. (C) SEC of purified TMEM24 SMP domain preincubated with liver PI indicates that PI binds and comigrates with TMEM24 SMP. Although TMEM24 SMP migrates as a dimer in solution, a small shift in apparent molecular weight upon binding to PI occurs, consistent with a change in conformation but not oligomerization state. (D) Analysis of individual fractions from 14.0 to 16.0 ml by SDS-PAGE confirms redistribution of the liganded SMP domain. (E) Fractions between 14.0 and 16.0 ml retention volume were pooled; lipid was extracted and resolved by thin-layer chromatography. The PI band did not appear in these fractions when TMEM24 SMP or liver PI was subjected separately to SEC.
