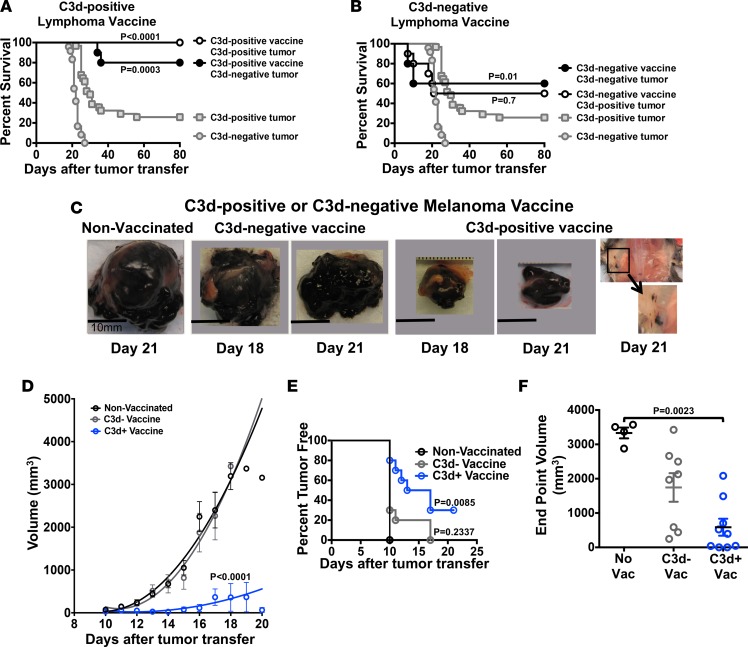
Figure 2. Adaptive immunity evoked by vaccination with killed C3d+ tumor cells protects against lymphoma and melanoma.
Mice were vaccinated with 1 × 107 C3d+ (n = 10) or C3d– (n = 10) killed lymphoma followed by administration of living 5 × 103 C3d+ or C3d– lymphoma cells 35 days later (A and B), or with 1 × 107 C3d+ (n = 10) or C3d– (n = 10) killed melanoma cells followed by transfer of 2 × 105 live melanoma cells 35 days later (C–F). (A) Survival of mice vaccinated with killed C3d+ lymphoma cells. (B) Survival of mice vaccinated with killed C3d– lymphoma cells. Note, the C3d-positive tumor and C3d-negative tumor groups in (A) and (B) are the same data as presented in Figure 1A. The data were not collected contemporaneously as the other groups in (A) and (B), but are shown here for reference. (C) Photographs of C3d– melanoma tumors excised at indicated days after tumor inoculation in mice vaccinated with C3d+ or C3d– irradiated melanoma cells. Shown also is a photograph of an incipient tumor growing s.c. (inset) in mice vaccinated with C3d+ melanoma cells, 21 days after tumor inoculation. (D) Impact of C3d+ or C3d– vaccine on growth of C3d– melanoma. Data represent mean ± SEM. Analysis was by Mann Whitney 2-tailed test. (E) Prevention of C3d– melanoma by vaccination with killed C3d+ or C3d– melanoma cells. Shown are Kaplan-Meier plots, and differences between curves were analyzed by the log rank Mantel-Cox test. (F) Impact of vaccination on growth of C3d– melanoma estimated by tumor size at death (sacrifice) or at 21 days in mice that were alive at 21 days. All nonvaccinated mice and 8 of 10 mice vaccinated with C3d– melanoma died or were sacrificed at 18 or 19 days for humane reasons. Four of 10 C3d+-vaccinated mice either had no apparent tumors or smaller tumors at sacrifice (21 days). Data represent mean ± SEM. Analysis was by Mann Whitney 2-tailed test.