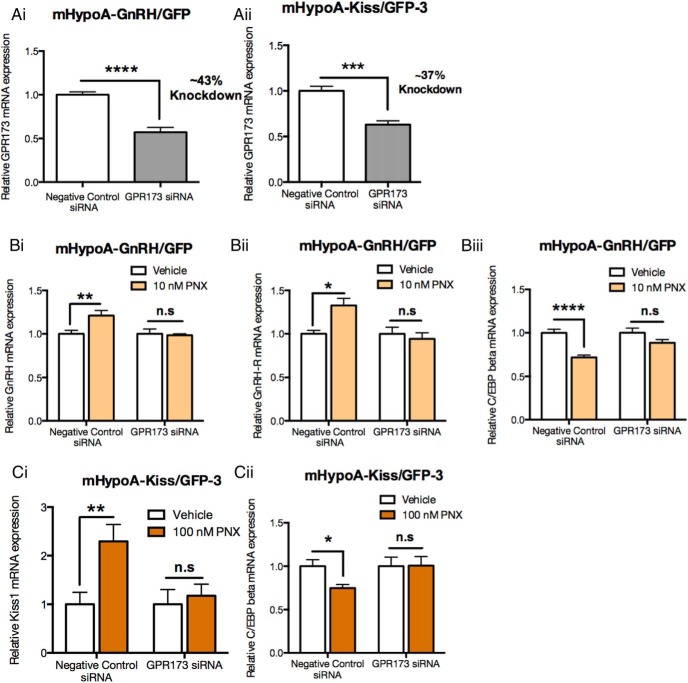
Figure 6. Knockdown of GPR173 expression impairs PNX-mediated regulation of reproductive genes in the mHypoA-GnRH/GFP and mHypoA-Kiss/GFP-3 cell models.
A, Cell models were transfected with either 30 nM of nontargeting negative control siRNA or GPR173 targeting siRNA for 48 hours, and then GPR173 mRNA expression was measured by quantitative real-time PCR. GPR173 mRNA expression was reduced by 43% in the mHypoA-GnRH/GFP cell model (Ai) and by 37% in the mHypoA-Kiss/GFP-3 cell model (Aii) with the GPR173 siRNA. B, The mHypoA-GnRH/GFP cell model was treated with 10 nM PNX for 2 hours after a 48-hour transfection with either negative control nontargeting siRNA or GPR173 targeting siRNA. RNA was isolated and mRNA expressions of GnRH (Bi), GnRH-R (Bii) and C/EBP-β (Biii) were measured using quantitative real-time PCR. The mHypoA-Kiss/GFP cell model was treated with 100 nM PNX for 24 hours after a 48-hour transfection with either negative control nontargeting siRNA or GPR173 targeting siRNA. The RNA was isolated, and the mRNA expressions of Kiss1 (Ci) and C/EBP-β (Cii) were measured using quantitative real-time PCR. The mRNA levels were normalized to the housekeeping gene histone 3a. Results are expressed as mean ± SEM (n = 4–9 independent experiments). *, P < .05; **, P < .01; ***, P < .001; ****, P < .001. n.s., not significant. Statistical significance was determined by a two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni's post hoc test or a Student's t test.