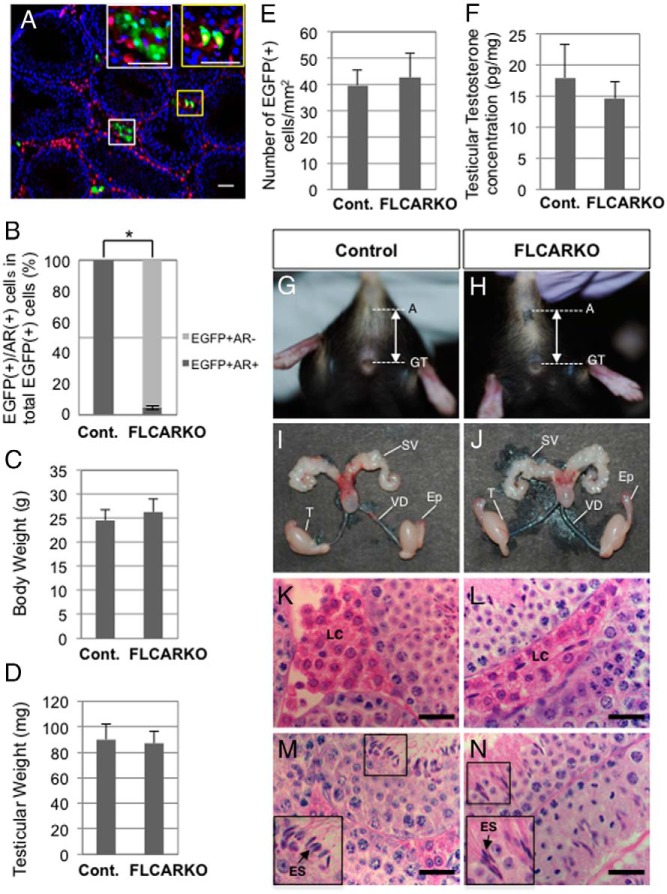
Figure 5. Phenotypes of FLCARKO mice at P56.
A, FLCARKO mice harboring the CAG-CAT-EGFP transgene were generated, and P56 testes were subjected to immunofluorescence analyses with antibodies against EGFP (green) and AR (red). The areas in the white and yellow rectangles were enlarged to show EGFP(+)/AR(−) cells and EGFP(+)/AR(+) cells, respectively, in the insets. B, The ratios of EGFP(+)/AR(−) cells to EGFP(+)/AR(+) cells in control (mFLE-Cre;CAG-CAT-EGFP) mice (n = 4) and FLCARKO mice harboring the CAG-CAT-EGFP transgene (n = 4) were calculated and plotted as mean ± SEM. *, P < .05, significant difference. C, The body weights were measured in control mice (n = 15) and FLCARKO mice (n = 11) and plotted as mean ± SEM. D, The testicular weights were measured in control mice (n = 30) and FLCARKO mice (n = 22) and plotted as mean ± SEM. E, The numbers of EGFP-positive cells in control mice and FLCARKO mice harboring the CAG-CAT-EGFP transgene (n = 4 for each) were counted, and the cell numbers per unit area were plotted as mean ± SEM (control, 39.8 ± 5.8; FLCARKO, 42.7 ± 9.5). F, The testicular testosterone concentrations in control mice and FLCARKO mice (n = 3 for each) were determined by LC-MS/MS analyses and plotted as mean ± SEM. G and H, Representative photos showing the external genitalia of control mice (G) and FLCARKO mice (H). Bidirectional arrows indicate anogenital distances. A, anus; GT, genital tubercle. I and J, Representative photos showing the internal genitalia of control mice (I) and FLCARKO mice (J). Ep, epididymis; SV, seminal vesicle; T, testis; VD, vas deferens. K–N, Control testes (K and M) and FLCARKO testes (L and N) were collected at P56 and subjected to H&E staining to show the histological features of the interstitial space (K and L) and seminiferous tubules (M and N). Small areas in M and N were enlarged to show the elongated spermatids (ESs) (arrows) in the insets. LC, Leydig cell. Scale bars, 50 μm.