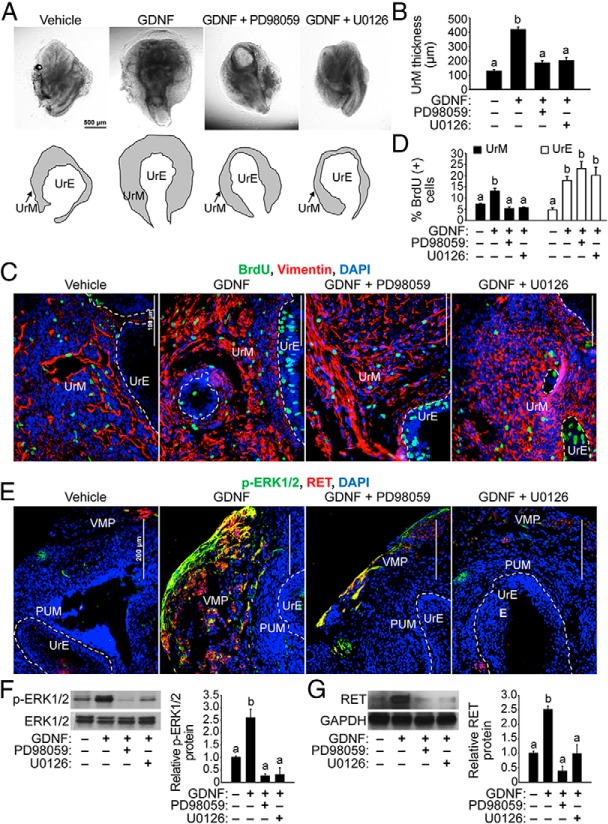
Figure 7. Inhibition of MEK1/2 kinase activity suppresses GDNF-induced proliferation of UrM cells.
A, E15.5 UGSs were cultured with vehicle control or 100 ng/mL GDNF in the presence or absence of 20 μM MEK inhibitor (PD98059 or U0126) for 7 days. UGSs were imaged at the same magnification. Below the images, the boundary of the UrM has been traced (black lines) and labeled to distinguish it from the UrE. B, Quantification of the average UrM thickness using six linear bilateral measurements of the UrM indicates that GDNF induced UrM thickening and both PD98059 and U0126 inhibited GDNF action in UrM thickening (n = 3–5). C, E15.5 UGSs were cultured with vehicle control or 100 ng/mL GDNF in the presence or absence of 20 μM MEK inhibitor (PD98059 or U0126) for 7 days, and 10 μM BrdU was added 2 hours prior to tissue processing for immunohistochemistry. Immunodetection of BrdU-positive cells (green) and vimentin-positive mesenchymal cells (red) and DAPI-stained nuclei (blue) shows an increase in BrdU-positive UrM and UrE cells in UGSs treated with GDNF. However, fewer BrdU-positive UrM cells were observed in UGSs cotreated with GDNF and PD98059 or U0126 compared with GDNF alone. D, Quantification of the percentage of BrdU-positive cells in vimentin-positive UrM and vimentin-negative UrE indicates that GDNF-induced proliferation of UrM cells was suppressed by MEK inhibitors PD98059 and U0126. In addition, the UrE showed similar increases in GDNF-induced proliferation in the presence and absence of each MEK inhibitor (n = 6). E, E15.5 UGSs were exposed for 48 hours to each MEK inhibitor compared with vehicle control, and the localization of p-ERK1/2 and RET proteins was determined using immunohistochemistry and fluorescence microscopy. Immunodetection of p-ERK1/2 (green) and RET (red) and DAPI-stained nuclei (blue) shows increased levels of these proteins in UGS treated with GDNF compared with vehicle control and abundant colocalization of p-ERK1/2 and RET in the VMP. Cotreatment of UGSs with PD98059 or U0126 suppressed the enrichment of p-ERK1/2 and RET proteins in response to GDNF and the colocalization of these proteins in the VMP. The boundaries between the PUM and UrE have been traced (dashed white line), and the VMP has been labeled. F, E15.5 UGSs were cultured with vehicle control or 100 ng/mL GDNF in the presence of absence of each MEK inhibitor for 48 hours, and immunoblot analysis of UGS lysates show that PD98059 and U0126 indeed suppressed the increase in p-ERK1/2 levels due to GDNF treatment. Relative p-ERK1/2 to total ERK1/2 protein ratios are shown using the mean and SEM (n = 5). G, PD98059 and U0126 also suppressed the increase in RET protein expression due to GDNF treatment. Relative RET to GAPDH protein ratios are shown using the mean and SEM (n = 5). The scale bars represent 500 μm (A), 100 μm (C) or 200 μm (E).