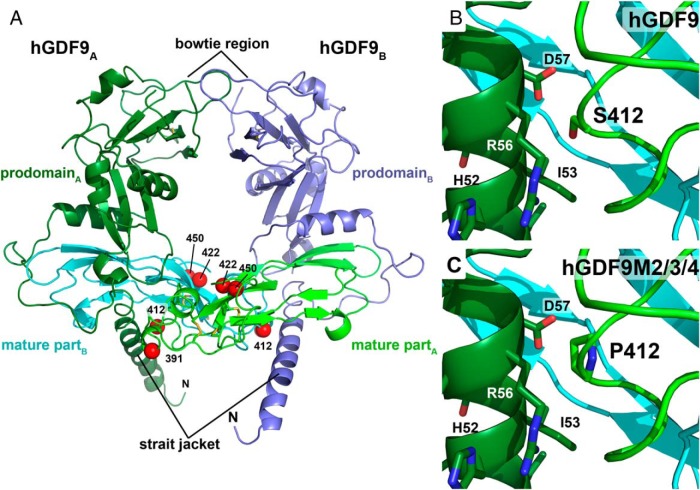
Figure 6. 3D homology model of the proprotein complex of human GDF9.
The model was obtained using the crystal structure of pro-TGFβ1 as template. A, Ribbon plot of the homodimeric GDF9 colored in light/dark green (chain A) and blue/cyan (chain B). The mature region, which is released upon proteolytic processing of the proprotein at a conserved R-X-K/R-R site, is colored in light green and cyan. The prodomain engaging in a strait jacket–like interaction with the mature region, is marked in dark green and blue. The disulfide bonds of the characteristic cystine knot are shown as yellow sticks. Red spheres mark the Cα-carbon position of the mutations introduced to form the human-mouse GDF9 chimeras M1 to M4. B, Magnification around amino acid Ser412 located in the mature region of hGDF9 showing its close proximity to helix α1 of the prodomain. C, Exchange of Ser412 by proline, the equivalent residue in murine GDF9, possibly weakens this interaction and hence the pro/mature complex leading to a decreased latency for GDF9 chimeras M2 to M4.