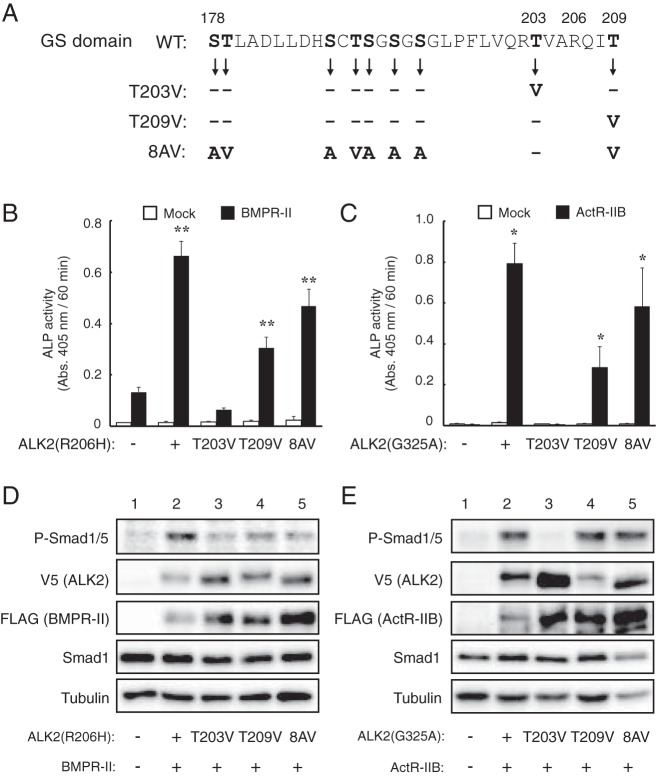
Figure 7. Thr203 of ALK2 is a crucial residue for the type II receptor-dependent enhancement of ALK2.
A, Amino acid sequences of the GS domains of WT and mutant ALK2. Of the nine Ser and Thr residues (in bold) present in WT ALK2, Thr203, Thr209, or the eight residues other than Thr203 were mutated to Ala and Val residues in the T203V, T209V, and 8AV mutants, respectively. These mutations were introduced in ALK2(R206H) and ALK2(G325A), and their activity was analyzed. B and C, Cooperative induction of ALP activity in C2C12 cells by type II receptors and mutant ALK2 constructs bearing mutations in the GS domain. ALK2(R206H) (B) and ALK2(G325A) (C) carrying the T203V, T209V, and 8AV mutations (or empty vector) were cotransfected with BMPR-II (B) and ActR-IIB (C), respectively. ALP activity was determined on day 3. The data are expressed as the mean ± SD (n = 3). *, P < .05 and **, P < .01 vs mock-transfected cells (Student's t test). D and E, Whole-cell lysates from C2C12 cells transfected with the indicated ALK2 and BMPR-II (D) or ActR-IIB (E) constructs were analyzed via a Western blot analysis with antibodies against phospho-Smad1/5, V5-tag (ALK2), FLAG-tag (type II receptors), Smad1, and tubulin.