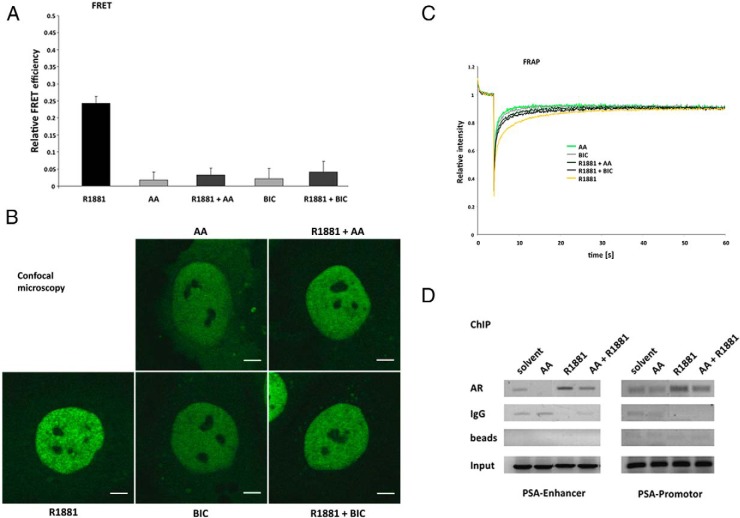
Figure 2. AA prevents AR N/C-terminal interaction and reduces the agonist-induced intranuclear foci formation and inhibits immobilization of AR.
Hep3B cells stably expressing tagged AR were cultured in CSS medium for 24 hours with R1881 (10−9 M), AA (10−4 M), or BIC (10−6 M) or cotreatment of the antagonists with the androgen R1881. A, FRET assay measurements indicate intramolecular AR N/C interaction inhibited by treatment with AA. The apparent FRET efficiency of YFP-AR-CFP is calculated as the fraction of CFP increase after YFP bleaching (acceptor photobleaching FRET). For normalization cells were transiently transfected with a plasmid for a CFP-YFP fusion construct (equal to 1) and cells cotransfected with CFP and YFP (equal to 0). Values for the treated samples represent the average ± SEM of at least 40 cells measured in three independent experiments. B, High-resolution confocal images of representative nuclei of Hep3B cells expressing GFP-AR at physiological levels after treatment with the indicated compounds. Scale, 5 μm. C, FRAP assays indicate the intranuclear mobility of GFP-AR. In strip-FRAP measurements, fluorescent molecules in a narrow strip spanning the nucleus were bleached for 100 msec at the maximum laser power. Subsequently, fluorescence in the strip was monitored every 100 msec. Fluorescence intensities were plotted against time and normalized to the prebleach value. The mean values of at least 40 cells measured in three independent experiments are plotted. D, AA reduces AR chromatin recruitment to AREs in the PSA promoter and enhancer of human PCa LNCaP cells. ChIP experiments were applied to detect the recruitment of AR at the endogenous PSA promoter and enhancer region in LNCaP cells. Cells were cultured in 10% CSS medium for 3 days and incubated with R1881 (10−10 M) or AA (3 × 10−5 M) or cotreated for 2 hours. The experiment was performed with an AR-specific antibody as well as IgG or without antibody (only beads) as control.