Figure 3.
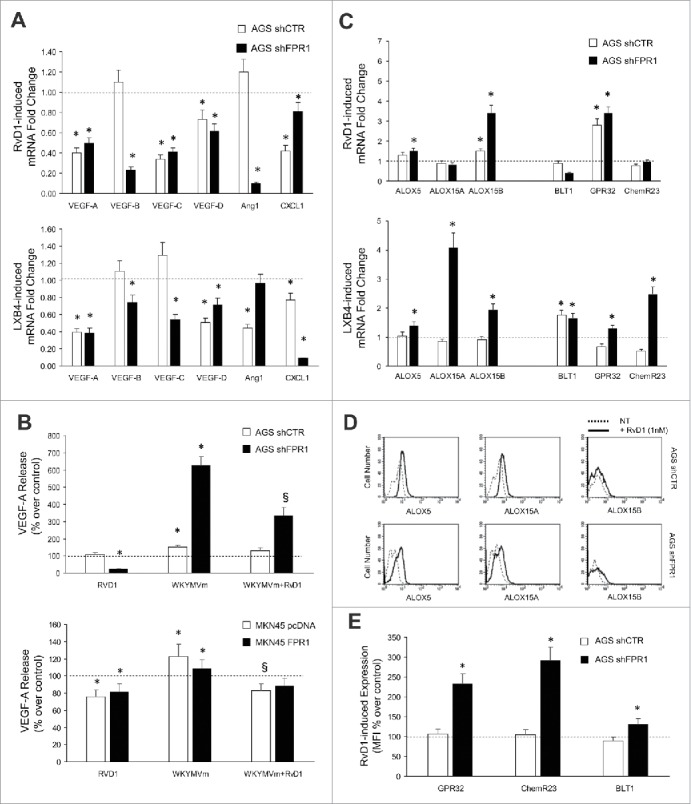
Anti-angiogenic effects of SPMs in GC. (A) RvD1 (1 nM) and LXB4 (1 nM) treatment significantly reduced mRNA expression of pro-angiogenic molecules (VEGF-A, -B, -C, -D, Ang1, and CXCL1) in AGS shCTR and shFPR1 cells. Data are represented as mean ± SD of three independent experiments. *p < .05 compared to the relative untreated control (dotted line). (B) Reduction of spontaneous and WKYMVm-induced VEGF-A release upon RvD1 treatment of the indicated GC cells. Data are represented as mean ± SD of three independent experiments. *p < .05 vs. the relative untreated control (dotted line). (C) RvD1 and LXB4 treatment significantly induced the mRNA expression of the enzymes (ALOX5, ALOX15A, and ALOX15B) and receptors (BLT1, GPR32, and ChemR23) involved in pro-resolving pathways in AGS shCTR and shFPR1 cells. Data are represented as mean ± SD of three independent experiments. *p < .05 vs. the relative untreated control (dotted line). (D) RvD1 treatment significantly induced ALOX5, ALOX15A, and ALOX15B protein expression in AGS shCTR and shFPR1 cells, as evaluated by cytofluorimetric analysis. One representative experiment out of three is shown. (E) RvD1 treatment significantly induced GPR32, ChemR23, BLT1 protein expression in AGS shCTR and shFPR1 cells, as assessed by cytofluorimetric analysis. Data are represented as mean ± SD of three independent experiments. *p < .05 compared to the relative untreated control (dotted line).
