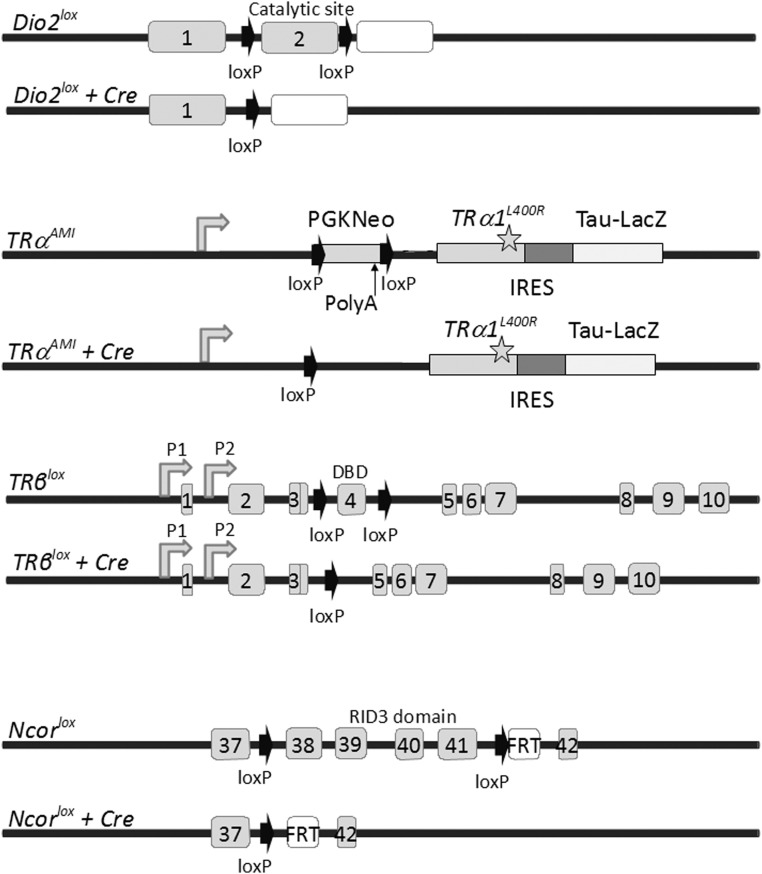
Figure 1.
Floxed alleles of genes with a specific function in TH signaling and their Cre-mediated recombination products. Cre recombination deletes the Dio2lox from the exon encoding the catalytic domain of type 2 deiodinase (90). Elimination of Dio2 prevents the local deiodination of T4 and produces a local T3 deficiency, in several tissues, including several brain areas, skeletal muscle, skin, pituitary, inner ear, and adipose tissues. The TRαAMI allele (84) carries a floxed cassette with polyadenylation signal, preventing expression of a downstream cDNA encoding the TRα1L400R dominant-negative mutant receptor receptor (mutation is indicated by the star). Cre-mediated recombination eliminates the cassette and triggers TRα1L400R expression in virtually any cell type because Thra expression is nearly ubiquitous. The IRES-TauLacZ cassette was introduced to monitor recombination by testing for β-galactosidase activity, which is, however, too low for easy detection. Therefore, assessment of recombination usually relies on the presence of a supplementary reporter transgene (122, 123). Because a strong phenotype is observed in heterozygous mice, new Cre/TRαAMI combinations can be generated within a single mouse generation. TRβlox (101) allows the elimination of exon 4 encoding the DNA-binding domain (DBD) shared by TRβ1 and TRβ2 and introduction of a frameshift for translational arrest. P1 and P2 are transcription promoters for TRβ1 and TRβ2 mRNA transcription. It can be used to eliminate TRβ1/2-mediated response in cells that express this receptor: hepatocytes, cardiomyocytes, pituitary thyrotropes, retina photoreceptors, etc. Cre recombination of the Ncor1lox allele (86) eliminates only exons encoding the RID3 domain of the corepressor that is required for TR interaction without changing the reading frame. Therefore, the NCoR1ΔID mutation preserves interactions with some other nuclear receptors and has limited developmental consequences. The mutation increases the sensitivity to T3 stimulation of the cells, such as hepatocytes, in which NcoR is a predominant corepressor. IRES, internal ribosome entry site; PGK, phosphoglycerate kinase; RID, receptor interaction domain.