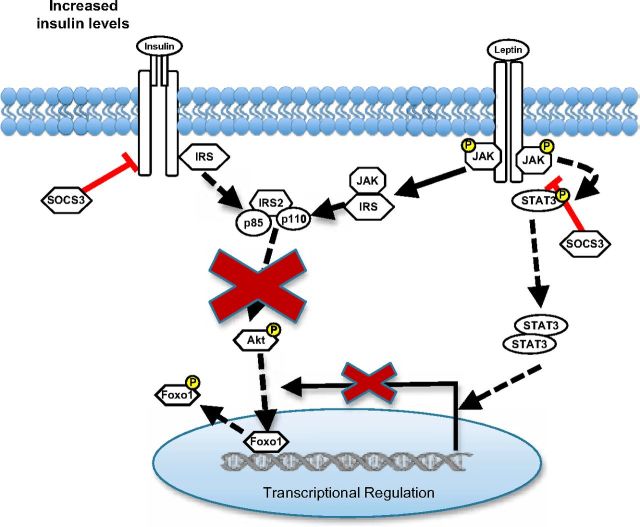
Figure 9.
Model of the putative role of central insulin resistance in attenuating leptin modulation of rHypoE-19 hypothalamic neurons. Chronic insulin stimulation attenuates activity of the PI3K pathway by hindering phosphorylation of Akt that may be required leptin-mediated transcriptional regulation of neurons. In addition, chronic stimulation of the insulin receptor may lead to an increase in SOCS3 protein levels, which are known to hinder both leptin and insulin signal transduction by dephosphorylation of the insulin receptor, JAK, STAT, and IRS proteins. This may, in part, account for the observed decrease in leptin-induced phosphorylation of Akt and STAT3 after induction of insulin resistance.