Abstract
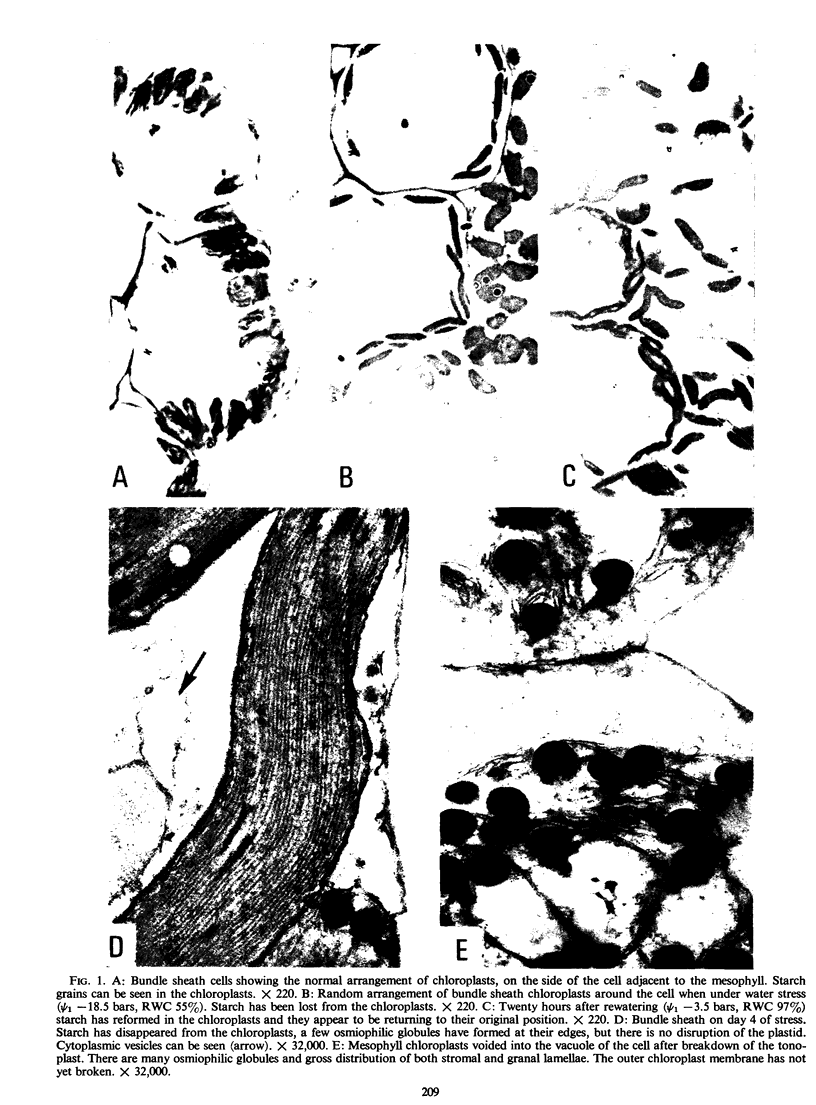
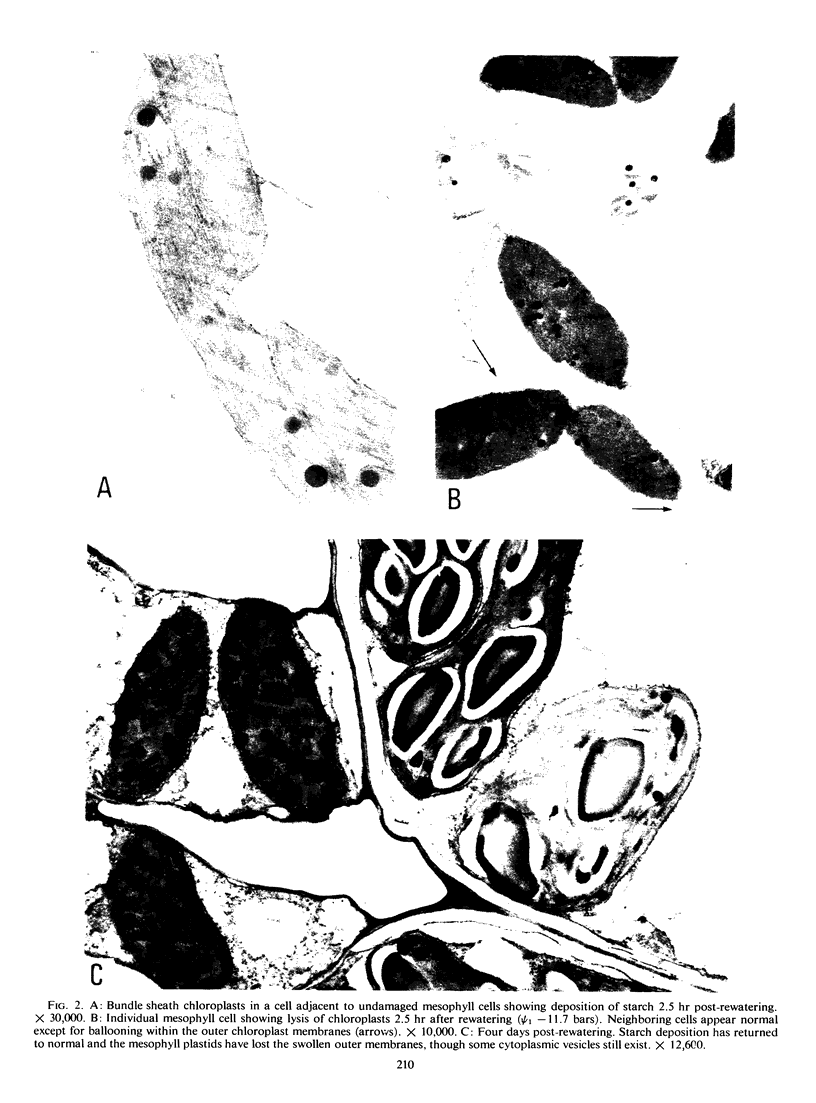
Ultrastructural changes were correlated with leaf water potential, relative water content, and abscisic acid levels in the leaf. Mesophyll cells were more prone to damage than bundle sheath cells at a leaf water potential of -18.5 bars. Tonoplast breakdown and cell disruption occurred in 25% of the mesophyll cells. On rewatering, these disrupted cells did not recover. In bundle sheath cells, starch, lost at about -13.5 bars leaf water potential, reappeared within 2.5 hours of rewatering.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boyer J. S. Leaf water potentials measured with a pressure chamber. Plant Physiol. 1967 Jan;42(1):133–137. doi: 10.1104/pp.42.1.133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanemasu E. T., Thurtell G. W., Tanner C. B. Design calibration and field use of a stomatal diffusion porometer. Plant Physiol. 1969 Jun;44(6):881–885. doi: 10.1104/pp.44.6.881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez-Diaz M. F., Kramer P. J. Behavior of Corn and Sorghum under Water Stress and during Recovery. Plant Physiol. 1971 Nov;48(5):613–616. doi: 10.1104/pp.48.5.613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholander P. F., Hammel H. T., Hemmingsen E. A., Bradstreet E. D. HYDROSTATIC PRESSURE AND OSMOTIC POTENTIAL IN LEAVES OF MANGROVES AND SOME OTHER PLANTS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Jul;52(1):119–125. doi: 10.1073/pnas.52.1.119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]