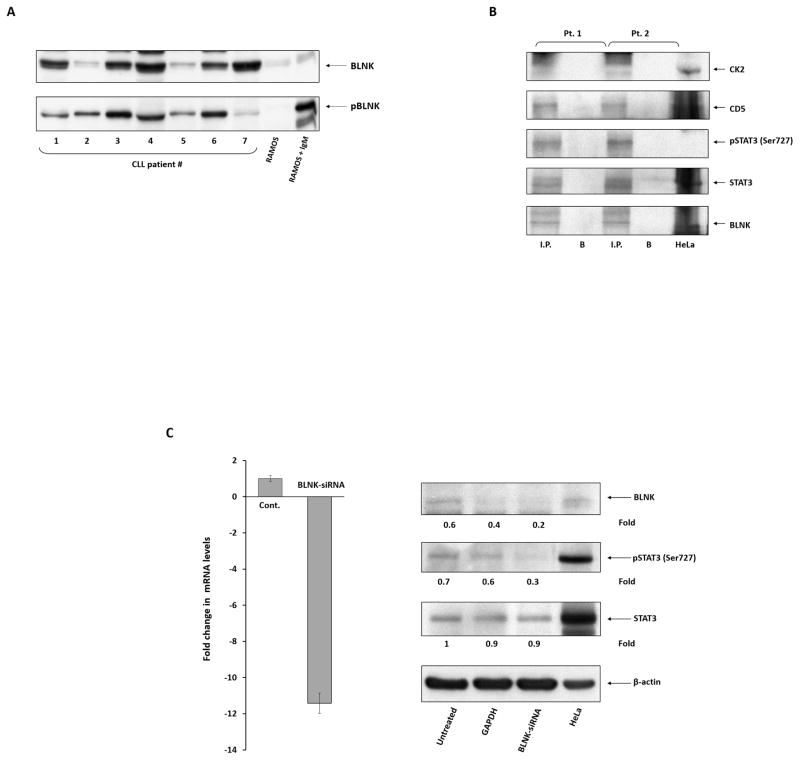
Figure 3. BLNK is required for CK2-induced phosphorylation of STAT3 in CLL cells.
(A) BLNK is constitutively phosphorylated in CLL cells. We obtained PB CLL cells from seven randomly selected CLL patients and, using Western immunoblotting, detected tyrosine pBLNK in all samples. Equal loading was confirmed by Ponceau staining (not shown). Untreated and IgM-treated RAMOS cells were used as controls. IgM: immunoglobulin M. (B) CK2, CD5, STAT3, and serine pSTAT3 co-immunoprecipitated with BLNK. CLL cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-BLNK antibodies. The immune complex was separated using SDS-PAGE, and STAT3, serine pSTAT3, CK2, and CD5 were detected in the immunoprecipitate by Western immunoblotting. I.P., immunoprecipitate; B, beads. (C) BLNK-siRNA inhibits the phosphorylation of STAT3 on serine residues. CLL cells from three different patients were transfected by electroporation with BLNK-siRNA or GAPDH or were left untreated (controls). Left panel: BLNK-siRNA significantly reduced BLNK mRNA levels. qRT-PCR was used to detect BLNK transcripts. The δ-δ cycle threshold method was used to determine the relative fold change in BLNK transcripts after treatment with BLNK-siRNA. Right panel: CLL cells transfected with BLNK-siRNA or GAPDH were analyzed using Western immunoblotting. As shown, BLNK-siRNA, but not GAPDH, significantly reduced the protein levels of BLNK and serine pSTAT3, whereas the levels of STAT3 remained unchanged by either treatment. HeLa cells were used as positive controls.