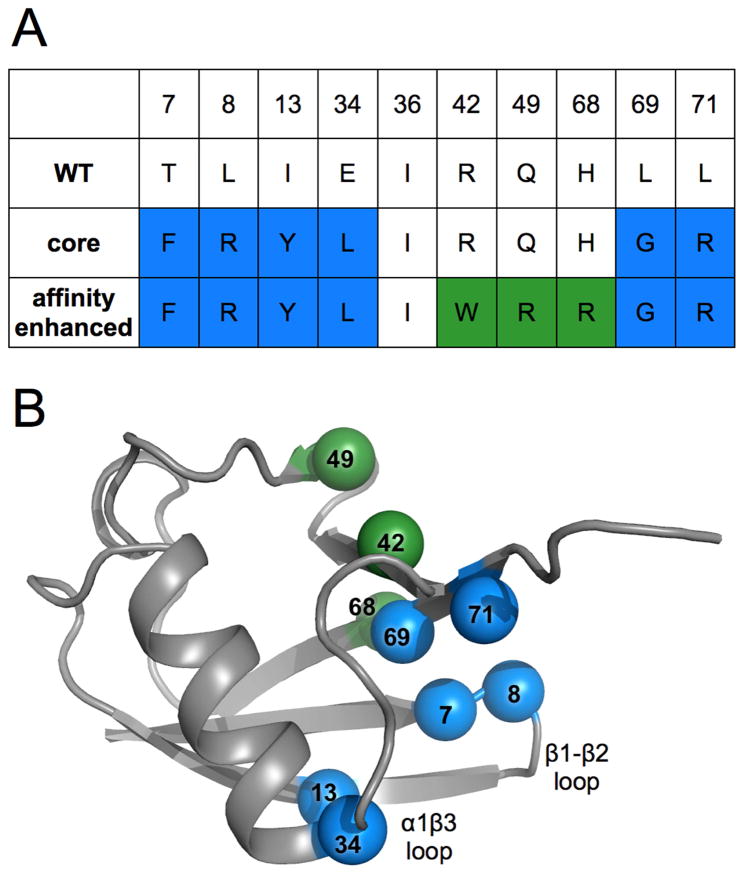
Figure 1. Locations and identities of mutations made across directed evolution trajectory of ubiquitin.
A) Table showing amino acid identities of mutation sites for the wild-type, core and affinity matured mutants. Blue coloring represents residue identities first introduced in the core mutant. Green shows new residue identities for the affinity matured mutations.
B) Wild-type ubiquitin (PDB ID: 1ubq) model shown in grey with spheres representing locations of mutation sites, colored as in panel A and labeled by residue number.