Fig. 3.
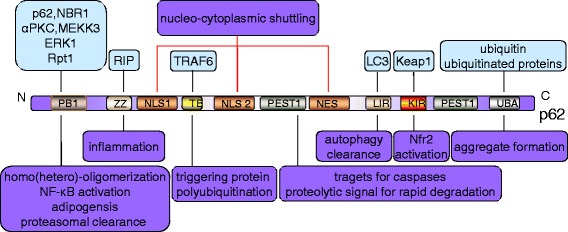
Structure and function of p62. The light blue block charts represent the interacting proteins and the light purple ones represent the function. p62 can assemble via the N-terminal PB1 domain (Phox and Bem1) with itself or with NBR1, termed homo- or hetero-oligomerization, respectively. The PB1 domain also interacts with atypical PKC (αPKC) and MEKK3, accounting for NF-κB activation with ERK1 and Rpt1 for adipogenesis and proteasomal clearance, respectively. The ZZ domain binds RIP1 kinase, which is responsible for inflammation. The TRAF6-binding domain (TB) interacts with TRAF6 proteins to trigger protein polyubiquitination. The nuclear localization signal (NLS1/2) and the export motif (NES) are involved in the nucleo-cytoplasmic shuttling of p62. PEST1 serves as a proteolytic signal for rapid degradation relevant to short-lived proteins and as targets for caspases. Through the LIR and the UBA, p62 assists in the autophagic degradation of ubiquitinated proteins. KIR binding to Keap1 leads to Nrf2 activation
