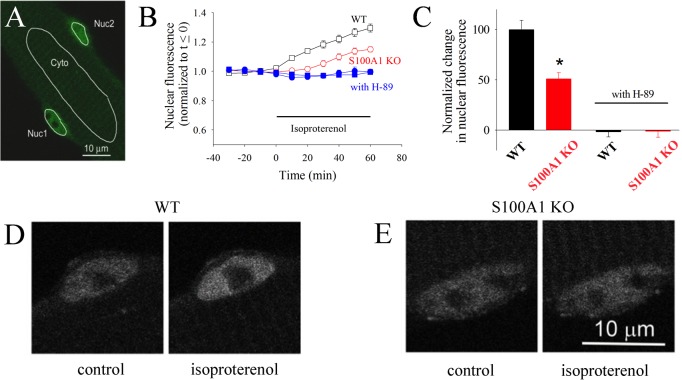
Figure 5.
HDAC4 nuclear localization is dependent on PKA and S100A1. (A) Confocal microscope image of a live resting skeletal muscle fiber expressing HDAC4-GFP. Nuc1 and Nuc2 are the areas of interest monitored in two different nuclei in the same muscle fiber. Cyt is a cytoplasmic area of interest. (B) Time course of nuclear HDAC4-GFP mean pixel fluorescence in muscle fibers from wild-type (empty black squares) or S100A1KO (empty red circles) mice, before and during application of isoproterenol (5 μM). Filled blue symbols give the time course of nuclear HDAC4-GFP in wild-type (filled squares) or S100A1KO (filled circles) muscle fibers exposed to isoproterenol after pre-exposure to PKA inhibitor H89 (5 μM), which completely blocks the increase in the leve of nuclear HDAC4-GFP. Error bars are SEM and are smaller than the size of the symbol when not shown. (C) The difference in nuclear HDAC due to β-adrenergic stimulation is significantly larger in wild-type than in S100A1KO muscle fibers. An asterisk indicates p < 0.05 from a two-sample t test. (D and E) Confocal images of exemplar nuclei expressing HDAC4-GFP before and after isoproterenol treatment for 60 min in a muscle fiber from the S100A1KO group and from a corresponding WT counterpart.