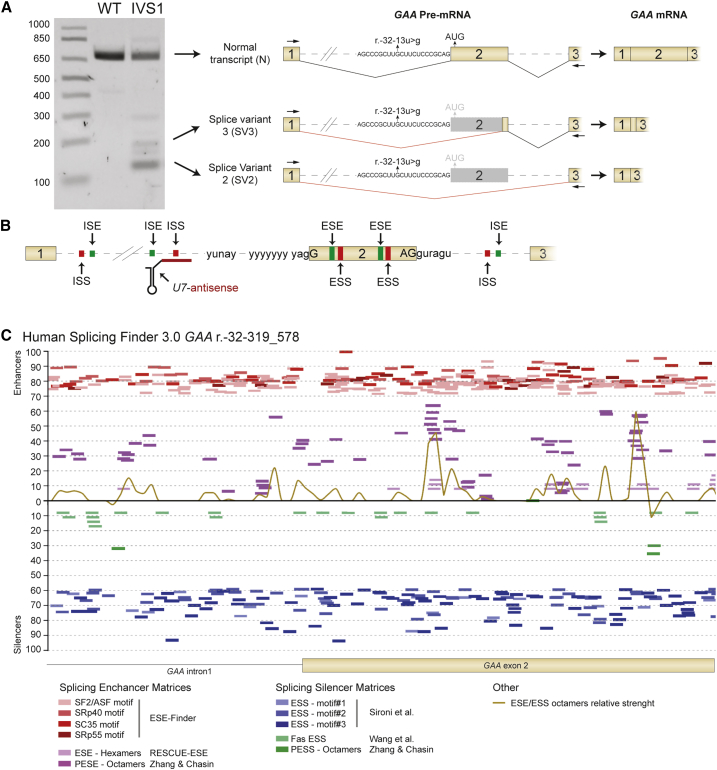
Figure 1.
In Silico Prediction to Identify Splicing Regulatory Elements Surrounding the IVS1 Variant
(A) Outline of the three major splicing products of the GAA pre-mRNA caused by the IVS1 variant in a patient-derived primary fibroblast. The gel illustrates the results of flanking exon RT-PCR analysis of GAA exon 2 using primers that anneal to exon 1 and exon 3. Loading from left to right is as follows: DNA size markers (in basepairs); WT indicates control fibroblasts and IVS1 denotes fibroblasts from patient 1. Cartoons of pre-mRNAs illustrate splicing events as described.24, 25, 26, 27 The location of the r.-32-13u>g (IVS1) variant in the pY tract is indicated. Spliced mRNA cartoons are shown on the far right. (B) Cartoon showing hypothetical splicing regulatory elements that may be subject to modulation (e.g., by a U7 snRNA). (C) In silico prediction in Human Splicing Finder 3.0 (http://www.umd.be/HSF3/) of exonic and intronic splicing silencers surrounding the GAA IVS1 variant. Algorithms used are indicated below the graph. PESE, putative exonic splicing enhancers; PESS, putative exonic splicing silencers.