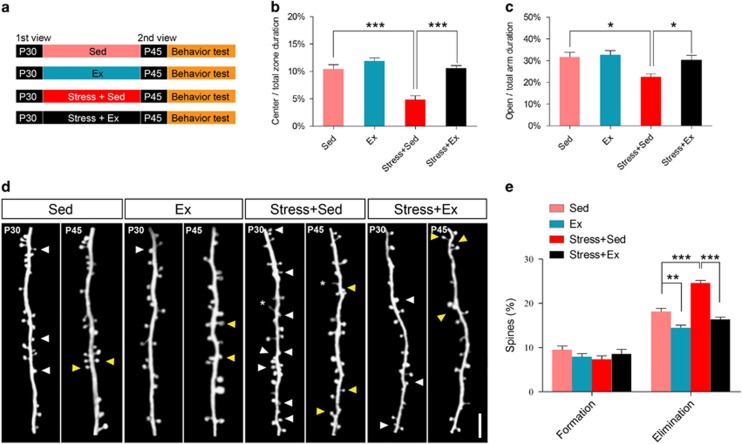
Figure 1.
Physical exercise alleviated stress-induced anxiety behavior and dendritic spine loss. (a) Schematic diagram showing stress induction by physical constrain and treadmill exercise (Ex, 1 h per day, 12 m min−1) or sedentary housing (Sed) for 14 consecutive days in Thy1-H line YFP mouse, plus two-photon imaging for the same region of barrel cortex. (b) Central time duration (%) during open-field test. (c) Time spent in open arm (%) during elevated plus maze test. (d) Imaging of the same dendritic branch on P30 and P45, including eliminated spines (white arrowhead), newly formed spines (yellow arrowhead) and filopodia (asterisk). (e) Percentage of spine formation and elimination on P45. Scale bar, 2 μm in d. Data were presented as mean±s.e.m. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 and ***P<0.001 using one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by Tukey post hoc test. Refer to Supplementary Table 1 for the number of animals and spines in each group. NS, no significant difference; YFP, yellow fluorescent protein.