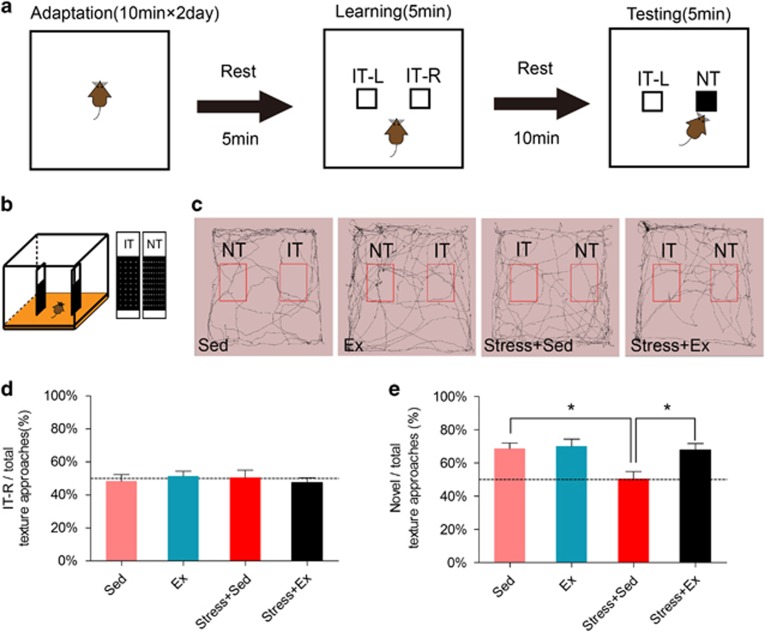
Figure 2.
Physical exercise prevented stress-induced working memory impairment in whisker-dependent novel texture discrimination task. (a) Schematic illustration of novel texture discrimination task. After a brief adaptation in the test arena (10 min, 2 days) and a short rest (5 min), the mice learned two identical textures (IT-L and IT-R) for 5 min. With different resting intervals (10, 30, 60 and 90 min), the animal was re-placed into the same arena, in which one novel texture (NT) was introduced instead of IT. (b) Test apparatus. IT and NT had identical size and color but different textures. (c) Movement paths of mice in test phase. Red lines represented arbitrary defined regions in which mice were recorded as approaching the texture. (d) Location preference of mice during the learning session. (e) Preference of mice for the novel texture in the testing session as calculated by the ratio of novel texture approaching time against total approaching time. Data were shown as mean±s.e.m. *P<0.05 using one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by Tukey post hoc test. N=6–7 animals per group.